WebKit
WKWebView
在一个客户端中,多个 WKWebView 实例共享一个 UI 进程(和 App 进程共享),共享一个 Networking 进程,每个 WKWebView 实例独享一个 WebContent 进程。
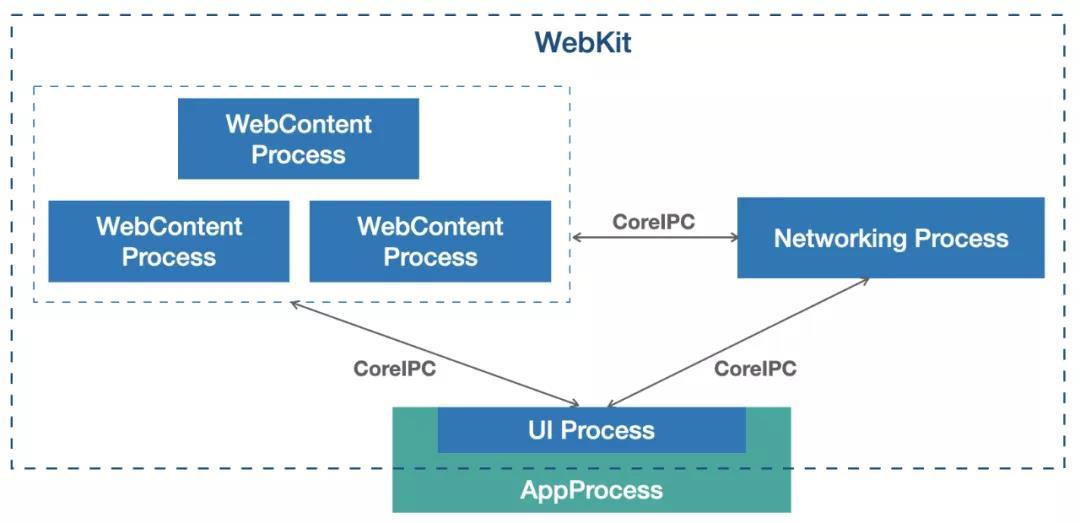
WebContent 进程负责将网页代码转换为用户可见的页面。解析 HTML 构建 DOM 树,解释和执行 JavaScript 代码,排版布局,提交绘制指令等。Safari 默认采用 “每标签页一进程” (Per-tab process) 的策略。如果一个网页(比如某个复杂的 Web App)崩溃了,只会导致这一个 WebContent 进程退出,该标签页变为空白,而不会导致整个浏览器或其他标签页崩溃。
Networking 进程负责所有的网络资源加载和管理。执行 DNS 查询、建立 HTTPS 连接,安全地存储和读取 Cookie。它作为�所有 WebContent 进程的共享资源,可以统一管理连接池,提高网络效率。
网页加载
Populating the page: how browsers work - Web performance | MDN
App 中的 Cookie 管理使用的 HTTPCookieStrorage,WKWebView 的 Cookie 管理使用的是 WKHttpCookieStore。这两个 Cookie 是可以同步的,但是同步会有明显的延迟。
对于 iOS 上,Cookie 文件有两种:
- bundleID.binarycookies 这是 HttpCookieStorage 持久化的 Cookie
- Cookies.binarycookies 这是 WKWebView 持久化的 Cookie
WebProcess 的 Cookie 如何同步到 App 进程?监听到 WKWebViewCookie 发生变化的时候,将 Cookie 同步到 App 进程。
func setupWebView() {
webView.configuration.websiteDataStore.httpCookieStore.add(self)
}
// WKHTTPCookieStoreObserver协议的方法
func cookiesDidChange(in cookieStore: WKHTTPCookieStore) {
cookieStore.getAllCookies { array in
array.forEach {
HTTPCookieStorage.shared.setCookie($0)
}
}
}
App 进程的 Cookie 如何同步到 WebProcess? HOOK NSHTTPCookieStorage 中读写 Cookie 的接口,并且监听网络请求中 "Set-Cookie" 关键字,在 App 进程 Cookie 发生变化时同步到 WKWebView。
Dark Mode
自己的网站想适配深色模式:sandoche/Darkmode.js: 🌓 Add a dark-mode / night-mode to your website in a few seconds
浏览器想对所有网站适配深色模式:darkreader/darkreader: Dark Reader Chrome and Firefox extension
网络请求拦截
网络请求拦截总是存在需求:缓存需求、监控需求、代理需求(大王卡免流)
重写 +[WKWebView handlesURLScheme:] 方法,将所有请求拦截:
+ (BOOL)handlesURLScheme:(NSString *)urlScheme {
return NO;
}
设置 -[WKWebViewConfiguration setURLSchemeHandler:forURLScheme:]
实现 @protocol WKURLSchemeHandler 的方法,用 NSURLSession 处理网络请求:
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView startURLSchemeTask:(id <WKURLSchemeTask>)urlSchemeTask;
- (void)webView:(WKWebView *)webView stopURLSchemeTask:(id <WKURLSchemeTask>)urlSchemeTask;
证书校验
NSURLProtectionSpace: A server or an area on a server, commonly referred to as a realm, that requires authentication.
Handling an authentication challenge | Apple Developer Documentation 服务器需要验证用户的身份,否则就会回 401 Forbidden。
Performing Manual Server Trust Authentication | Apple Developer Documentation(文章不长,多看几遍加深理解)
When you use a secure connection (such as https) with a URL request, your NSURLSessionDelegate receives an authentication challenge with an authentication type of NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust. Unlike other challenges where the server is asking your app to authenticate itself, this is an opportunity for you to authenticate the server’s credentials.
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session
task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task
didReceiveChallenge:(NSURLAuthenticationChallenge *)challenge
completionHandler:(void (^)(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeDisposition disposition, NSURLCredential *_Nullable credential))completionHandler {
if ([challenge.protectionSpace.authenticationMethod isEqualToString:NSURLAuthenticationMethodServerTrust]) {
NSString *host = challenge.protectionSpace.host;
if ([host isEqualToString:@"127.0.0.1"]) {
SecTrustRef serverTrust = challenge.protectionSpace.serverTrust;
NSURLCredential *credential = [NSURLCredential credentialForTrust:serverTrust];
completionHandler(NSURLSessionAuthChallengeUseCredential, credential);
return;
}
}
completionHandler(NSURLSessionAuthChallengePerformDefaultHandling, nil);
}