SDWebImage
UIView category
我们从一个常用的调用接口开始探索:
let url = URL(string: "...")
imageView.sd_setImage(with: url)
这是 UIImageView+WebCache 提供的其中一个接口,由于 Objective-C 不像 Swift 可以为函数声明默认参数值,因此需要声明多个接口。它们最终会汇合到这个方法:
- (void)sd_setImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
placeholderImage:(nullable UIImage *)placeholder
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDExternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
[self sd_internalSetImageWithURL:url
placeholderImage:placeholder
options:options
context:context
setImageBlock:nil
progress:progressBlock
completed:^(UIImage * _Nullable image, NSData * _Nullable data, NSError * _Nullable error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL * _Nullable imageURL) {
if (completedBlock) {
completedBlock(image, error, cacheType, imageURL);
}
}];
}
首先理解这个接口各参数的含义。
SDWebImageOptions 定义在 SDWebImageDefine.h,是图片下载的选项,用 bitmask 的形式表示:
typedef NS_OPTIONS(NSUInteger, SDWebImageOptions) {
/**
* By default, when a URL fail to be downloaded, the URL is blacklisted so the library won't keep trying.
* This flag disable this blacklisting.
*/
SDWebImageRetryFailed = 1 << 0,
}
SDWebImageContext 定义在 SDWebImageDefine.h,是对下载选项的一个扩充,This hold the extra objects which options enum can not hold. 它是一个字典,可以对图片 operation key、cache、loader、coder、transformer 等进行自定义。
typedef NSDictionary<SDWebImageContextOption, id> SDWebImageContext;
sd_internalSetImage 多了一个参数 @param setImageBlock If not provide, use the built-in set image code (supports UIImageView/NSImageView and UIButton/NSButton currently).
查看分类 @interface UIView (WebCache),这个分类中为 UIView 添加了几个属性:
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly, nullable) NSURL *sd_imageURL;
@property (nonatomic, strong, readonly, nullable) NSString *sd_latestOperationKey;
@property (nonatomic, strong, null_resettable) NSProgress *sd_imageProgress;
为分类添加属性的方法:
- (nullable NSURL *)sd_imageURL {
// selector 作为 key!
return objc_getAssociatedObject(self, @selector(sd_imageURL));
}
- (void)setSd_imageURL:(NSURL * _Nullable)sd_imageURL {
objc_setAssociatedObject(self, @selector(sd_imageURL), sd_imageURL, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_RETAIN_NONATOMIC);
}
接下来探索 @implementation UIView (WebCache) 中关键方法的实现。
下载图片的操作 SDWebImageOperation 会与当前 UIView 关联起来:
- (void)sd_internalSetImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
placeholderImage:(nullable UIImage *)placeholder
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
setImageBlock:(nullable SDSetImageBlock)setImageBlock
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
// 注意,这个函数是众多 UIView 接口背后的调用
// 其中 context 参数是 SDK 外部用户直接传参进来的
// 为了避免修改外部的参数,因此对它执行拷贝
if (context) {
// copy to avoid mutable object
context = [context copy];
} else {
context = [NSDictionary dictionary];
}
NSString *validOperationKey = context[SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey];
if (!validOperationKey) {
validOperationKey = NSStringFromClass([self class]); // 例如 "UIImageView"
}
self.sd_latestOperationKey = validOperationKey;
// 取消原先的操作
[self sd_cancelImageLoadOperationWithKey:validOperationKey];
if (url) {
id <SDWebImageOperation> operation = [manager loadImageWithURL:url options:options context:context progress:combinedProgressBlock completed:^(UIImage *image, NSData *data, NSError *error, SDImageCacheType cacheType, BOOL finished, NSURL *imageURL) {
dispatch_main_async_safe(^{
[self sd_setImage:targetImage imageData:targetData basedOnClassOrViaCustomSetImageBlock:setImageBlock transition:transition cacheType:cacheType imageURL:imageURL];
callCompletedBlockClosure();
});
}];
// 将这个 operation 与当前 UIView 实例关联起来!
[self sd_setImageLoadOperation:operation forKey:validOperationKey];
}
}
NSMapTable
关联 operation 定义在 UIView+WebCacheOperation,其本质是用一个字典存储当前 UIView 正在运行的操作 [operationKey: operation],有趣的是这里用到了 NSMapTable,它的初始化:
operations = [[NSMapTable alloc] initWithKeyOptions:NSPointerFunctionsStrongMemory valueOptions:NSPointerFunctionsWeakMemory capacity:0];
NSMapTable 类似于 NSDictionary,但它可以指定 key 和 value 的内存管理语义。
NSDictionary / NSMutableDictionary 对 key 拷贝,对 value 强引用。
NSMapTable 可以对键和值弱引用,当键或值当中的一个被释放时,这一键值对就会被移除掉。
NSDictionary 的 key 需要遵守 NSCopying 协议,当调用 NSMutableDictionary 的 - (void)setObject:(ObjectType)anObject forKey:(KeyType <NSCopying>)aKey; 方法时,会对 key 进行 copy。
留意 SDWebImageContextSetImageOperationKey 是可以由外部使用者设置的任意对象,这些对象不一定遵循 NSCopying,因此这里将 key 的内存管理语义指定为 NSPointerFunctionsStrongMemory。
同时,因为这里对 operation 是弱引用,当 key 对应的 operation 执行完毕被释放后,字典里的这一项也会自动被移除。
SDWebImageManager
接下来研究 [SDWebImageManager sharedManager] 和 loadImageWithURL: 接口。
SDWebImageManager 这个类是 UIView category 提供的接口背后真正完成工作的类。当然,我们也可以不通过 UIView 的接口而直接使用它。它结合了下载和缓存的两部分功能,它的初始化:
- (nonnull instancetype)init {
id<SDImageCache> cache = [[self class] defaultImageCache];
if (!cache) {
cache = [SDImageCache sharedImageCache];
}
id<SDImageLoader> loader = [[self class] defaultImageLoader];
if (!loader) {
loader = [SDWebImageDownloader sharedDownloader];
}
return [self initWithCache:cache loader:loader];
}
这里的 cache 和 loader 可以由外部自行指定,如果没有指定则使用框架内的默认实现类。
一、组合操作
- (SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)loadImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nonnull SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
// 组合操作:下载+缓存!
// 遵循 SDWebImageOperation 协议,operation 可以被 cancel,因此在后续的每一步骤中,都有对 operation 状态的检查
SDWebImageCombinedOperation *operation = [SDWebImageCombinedOperation new];
operation.manager = self;
// Preprocess the options and context arg to decide the final the result for manager
// 处理自定义项的优先顺序:
// self.optionsProcessor > 接口传参 context > self.transformer/cacheKeyFilter/cacheSerializer > default
SDWebImageOptionsResult *result = [self processedResultForURL:url options:options context:context];
// Start the entry to load image from cache
[self callCacheProcessForOperation:operation url:url options:result.options context:result.context progress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
return operation;
}
自定义项的优先顺序处理,类似于 Git Configuration 的分级处理,高优先级的选项会覆盖低优先级的选项(仓库 -> 用户 -> 系统)。
Git uses a series of configuration files to determine non-default behavior that you may want. The first place Git looks for these values is in the system-wide [path]/etc/gitconfig file, which contains settings that are applied to every user on the system and all of their repositories. If you pass the option --system to git config, it reads and writes from this file specifically.
The next place Git looks is the ~/.gitconfig (or ~/.config/git/config) file, which is specific to each user. You can make Git read and write to this file by passing the --global option.
Finally, Git looks for configuration values in the configuration file in the Git directory (.git/config) of whatever repository you’re currently using. These values are specific to that single repository, and represent passing the --local option to git config. If you don’t specify which level you want to work with, this is the default.
Each of these “levels” (system, global, local) overwrites values in the previous level.
二、查找缓存流程
- (void)callCacheProcessForOperation:
- 查找结果返回,不管是否命中,都进入下载流程
- 指定 SDWebImageFromLoaderOnly,不需要缓存,进入下载流程
- (void)callCacheProcessForOperation:(nonnull SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)operation
url:(nonnull NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
if (shouldQueryCache) {
NSString *key = [self cacheKeyForURL:url context:context];
@weakify(operation);
operation.cacheOperation = [imageCache queryImageForKey:key options:options context:context cacheType:queryCacheType completion:^(UIImage * _Nullable cachedImage, NSData * _Nullable cachedData, SDImageCacheType cacheType) {
@strongify(operation); // 解除 operation 引起的循环引用!
// Continue download process
[self callDownloadProcessForOperation:operation url:url options:options context:context cachedImage:cachedImage cachedData:cachedData cacheType:cacheType progress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
}];
}
}
三、下载流程
- (void)callDownloadProcessForOperation:
- 需要下载
- 命中缓存的情况下,下载完成,刷新缓存!
- 未命中缓存的情况下,下载完成,写入缓存!
- 不需要下载,返回缓存图片
- Image not in cache and download disallowed by delegate
- (void)callDownloadProcessForOperation:(nonnull SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)operation
url:(nonnull NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(SDWebImageContext *)context
cachedImage:(nullable UIImage *)cachedImage
cachedData:(nullable NSData *)cachedData
cacheType:(SDImageCacheType)cacheType
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
if (shouldDownload) {
if (cachedImage && options & SDWebImageRefreshCached) {
// 缓存命中
[self callCompletionBlockForOperation:operation completion:completedBlock image:cachedImage data:cachedData error:nil cacheType:cacheType finished:YES url:url];
// context 是不可变的,要想改变它需要经过以下的操作
SDWebImageMutableContext *mutableContext;
if (context) {
mutableContext = [context mutableCopy];
} else {
mutableContext = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
}
mutableContext[SDWebImageContextLoaderCachedImage] = cachedImage;
context = [mutableContext copy];
}
@weakify(operation);
operation.loaderOperation = [imageLoader requestImageWithURL:url options:options context:context progress:progressBlock completed:^(UIImage *downloadedImage, NSData *downloadedData, NSError *error, BOOL finished) {
@strongify(operation);
// Continue store cache process
// 下载完成,写入缓存!
[self callStoreCacheProcessForOperation:operation url:url options:options context:context downloadedImage:downloadedImage downloadedData:downloadedData finished:finished progress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
}];
}
}
四、写入缓存流程
- (void)callStoreCacheProcessForOperation:
- 缓存原始图像
- 要缓存到磁盘,先经过 cache serializer 处理
- 缓存完成后,进入 transform 流程
- (void)callStoreCacheProcessForOperation:(nonnull SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)operation
url:(nonnull NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(SDWebImageContext *)context
downloadedImage:(nullable UIImage *)downloadedImage
downloadedData:(nullable NSData *)downloadedData
finished:(BOOL)finished
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
BOOL shouldCacheOriginal = downloadedImage && finished;
// 有原始图像是一定会保存的
if (shouldCacheOriginal) {
if (cacheSerializer && (targetStoreCacheType == SDImageCacheTypeDisk || targetStoreCacheType == SDImageCacheTypeAll)) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0), ^{
@autoreleasepool {
// 要缓存到磁盘,先经过 cache serializer 处理
// The cache serializer is used to convert the decoded image, the source downloaded data, to the actual data used for storing to the disk cache.
NSData *cacheData = [cacheSerializer cacheDataWithImage:downloadedImage originalData:downloadedData imageURL:url];
// 调用 [imageCache storeImage:image imageData:data forKey:key cacheType:cacheType completion:...];
[self storeImage:downloadedImage imageData:cacheData forKey:key cacheType:targetStoreCacheType options:options context:context completion:^{
// Continue transform process
[self callTransformProcessForOperation:operation url:url options:options context:context originalImage:downloadedImage originalData:downloadedData finished:finished progress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
}];
}
});
}
}
}
五、transform 流程
缓存 transform 后的图片,完成全流程。
// Transform process
- (void)callTransformProcessForOperation:(nonnull SDWebImageCombinedOperation *)operation
url:(nonnull NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageOptions)options
context:(SDWebImageContext *)context
originalImage:(nullable UIImage *)originalImage
originalData:(nullable NSData *)originalData
finished:(BOOL)finished
progress:(nullable SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDInternalCompletionBlock)completedBlock {
if (shouldTransformImage) {
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_global_queue(DISPATCH_QUEUE_PRIORITY_HIGH, 0), ^{
@autoreleasepool {
UIImage *transformedImage = [transformer transformedImageWithImage:originalImage forKey:key];
if (transformedImage && finished) {
[self storeImage:transformedImage imageData:cacheData forKey:key cacheType:storeCacheType options:options context:context completion:^{
[self callCompletionBlockForOperation:operation completion:completedBlock image:transformedImage data:originalData error:nil cacheType:SDImageCacheTypeNone finished:finished url:url];
}];
}
}
});
}
}
框架提供了圆角、Resize、Cropping、Flipping、Rotate、Tint、Blur、Fliter 多种 transformer,还可以自由组合成 SDImagePipelineTransformer;通过 UIImage+Transform 分类提供实现。
下一步,我们分别探索 imageCache(查找缓存、写入缓存)和 imageLoader(下载)的实现。
SDImageCache
SDImageCacheDefine 定义了协议 @protocol SDImageCache,外部可以遵守这个协议并自行实现协议中的方法。如果不自定义的话,则会使用默认的实现类 SDImageCache。
我们知道 SDWebImageCombinedOperation 包含了两个操作 cacheOperation 和 loaderOperation,其中 cacheOperation 就是从这里创建的:
- (nullable NSOperation *)queryCacheOperationForKey:(nullable NSString *)key options:(SDImageCacheOptions)options context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context cacheType:(SDImageCacheType)queryCacheType done:(nullable SDImageCacheQueryCompletionBlock)doneBlock {
// First check the in-memory cache...
UIImage *image;
if (queryCacheType != SDImageCacheTypeDisk) {
image = [self imageFromMemoryCacheForKey:key];
// [self.memoryCache objectForKey:key];
}
// 如果指定只从内存中查找缓存,到这里就结束了
if (shouldQueryMemoryOnly) {
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(image, nil, SDImageCacheTypeMemory);
}
return nil; // 已完成查询,operation 返回 nil
}
// Second check the disk cache...
NSOperation *operation = [NSOperation new];
// block,取磁盘缓存可以是同步或异步执行
void(^queryDiskBlock)(void) = ^{
// 操作被取消的话这个 block 不会被执行
if (operation.isCancelled) {
if (doneBlock) {
doneBlock(nil, nil, SDImageCacheTypeNone);
}
return;
}
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *diskData = [self diskImageDataBySearchingAllPathsForKey:key];
// [self.diskCache dataForKey:key];
UIImage *diskImage;
if (image) {
// the image is from in-memory cache, but need image data
diskImage = image;
} else if (diskData) {
diskImage = [self diskImageForKey:key data:diskData options:options context:context];
// 在这里完成对图片的解码!
// 见 SDImageCacheDefine.m
// UIImage *image = SDImageCacheDecodeImageData(data, key, [[self class] imageOptionsFromCacheOptions:options], context);
// return image;
// 解码后的图片缓存到内存中!
if (diskImage && self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = diskImage.sd_memoryCost;
[self.memoryCache setObject:diskImage forKey:key cost:cost];
}
}
}
};
return operation;
}
在 SDMWebImageManager 第四步写入缓存流程时,会调用到 SDImageCache 的这个方法:
- (void)storeImage:(nullable UIImage *)image
imageData:(nullable NSData *)imageData
forKey:(nullable NSString *)key
toMemory:(BOOL)toMemory
toDisk:(BOOL)toDisk
completion:(nullable SDWebImageNoParamsBlock)completionBlock {
if (toMemory && self.config.shouldCacheImagesInMemory) {
NSUInteger cost = image.sd_memoryCost;
[self.memoryCache setObject:image forKey:key cost:cost];
}
if (toDisk) {
// 对文件的读写要放到同一个操作队列里
dispatch_async(self.ioQueue, ^{
@autoreleasepool {
NSData *data = imageData;
if (!data && image) {
// 没有原始 data,尝试获取图片格式,并进行编码
data = [[SDImageCodersManager sharedManager] encodedDataWithImage:image format:format options:nil];
}
// 写入磁盘
[self _storeImageDataToDisk:data forKey:key];
}
});
}
}
我们接着探索:内存缓存如何写入/读取?磁盘缓存如何写入/读取?图片如何解码?
SDMemoryCache
SDWebImage 声明了 @protocol SDMemoryCache <NSObject> 协议并提供了默认实现�。在框架中处处体现这样的面向协议编程设计思想。
NSCache
SDMemoryCache 继承自 NSCache,它有几个特点:
- 自动回收内存,当内存紧张时,自动移除键值对。
- 线程安全,操作无需加锁。
- 对 key 强引用,而不是 copy。
我们可以指定 NSCache 中的 countLimit (The maximum number of objects the cache should hold) 和 totalCostLimit (The maximum total cost, such as the size in bytes of the object, that the cache can hold),来控制缓存的容量,这两个属性默认值是 0,即无限制。
WeakMemoryCache
注意在 SDImageCacheConfig 中有一个选项 shouldUseWeakMemoryCache 默认开启。它的说明:SDMemoryCache will use a weak maptable to store the image at the same time when it stored to memory, and get removed at the same time. 当图片存入内存缓存的同时,也在这个哈希表里保存了一份弱引用。
When memory warning is triggered, since the weak maptable does not hold a strong reference to image instance, even when the memory cache itself is purged, some images which are held strongly by UIImageViews or other live instances can be recovered again, to avoid later re-query from disk cache or network. This may be helpful for the case, for example, when app enter background and memory is purged, cause cell flashing after re-enter foreground. 当内存紧张,内存缓存被清除时,有一些图片仍然会被正在显示的 UIView 强引用,这些内存不会回收,这时 weak memory cache 就起作用了。可以在下次查找缓��存时直接命中,而无需读取磁盘。
它同样使用 NSMapTable 实现,对它的操作需要加锁:
- (void)commonInit {
self.weakCache = [[NSMapTable alloc] initWithKeyOptions:NSPointerFunctionsStrongMemory valueOptions:NSPointerFunctionsWeakMemory capacity:0];
self.weakCacheLock = dispatch_semaphore_create(1);
}
小结
- 写入内存缓存:调用 NSCache 和 NSMapTable 的
setObject:forKey:方法。 - 读取内存缓存:调用 NSCache 的
objectForKey:方法,如果未命中,查询 NSMapTable。如果弱引用缓存命中,会同步到 NSCache 中! - 擦除内存缓存:调用 NSCache 和 NSMapTable 的
removeObjectForKey方法。
SDDiskCache
SDWebImage 声明了 @protocol SDDiskCache <NSObject> 协议并提供了默认实现。在框架中处处体现这样的面向协议编程设计思想。
查找磁盘缓存:
- (NSData *)dataForKey:(NSString *)key {
NSString *filePath = [self cachePathForKey:key];
NSData *data = [NSData dataWithContentsOfFile:filePath options:self.config.diskCacheReadingOptions error:nil];
return data;
}
写入磁盘缓存:
- (void)setData:(NSData *)data forKey:(NSString *)key {
if (![self.fileManager fileExistsAtPath:self.diskCachePath]) {
[self.fileManager createDirectoryAtPath:self.diskCachePath withIntermediateDirectories:YES attributes:nil error:NULL];
}
NSString *cachePathForKey = [self cachePathForKey:key];
NSURL *fileURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:cachePathForKey];
[data writeToURL:fileURL options:self.config.diskCacheWritingOptions error:nil];
// disable iCloud backup
if (self.config.shouldDisableiCloud) {
// ignore iCloud backup resource value error
[fileURL setResourceValue:@YES forKey:NSURLIsExcludedFromBackupKey error:nil];
}
}
SDDiskCache 还实现了计算文件占用大小、文件个数的相关方法。
如何移除过期的文件
- (void)removeExpiredData {
NSURL *diskCacheURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:self.diskCachePath isDirectory:YES];
// 第一轮清除:清除所有过期��的文件。如何定义“过期”?
// 可以自定义按照文件的哪个属性,来决定是否过期
NSURLResourceKey cacheContentDateKey = NSURLContentModificationDateKey;
NSArray<NSString *> *resourceKeys = @[NSURLIsDirectoryKey, cacheContentDateKey, NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
// 遍历缓存文件夹,获取所有文件的以上属性
NSDirectoryEnumerator *fileEnumerator = [self.fileManager enumeratorAtURL:diskCacheURL
includingPropertiesForKeys:resourceKeys
options:NSDirectoryEnumerationSkipsHiddenFiles
errorHandler:NULL];
NSDate *expirationDate = (self.config.maxDiskAge < 0) ? nil: [NSDate dateWithTimeIntervalSinceNow:-self.config.maxDiskAge];
NSMutableDictionary<NSURL *, NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *> *cacheFiles = [NSMutableDictionary dictionary];
NSUInteger currentCacheSize = 0;
// Enumerate all of the files in the cache directory. This loop has two purposes:
// 1. Removing files that are older than the expiration date. 清除所有过期文件!
// 2. Storing file attributes for the size-based cleanup pass. 记录文件属性,为第二轮清除做准备!
NSMutableArray<NSURL *> *urlsToDelete = [[NSMutableArray alloc] init];
for (NSURL *fileURL in fileEnumerator) {
NSError *error;
NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *resourceValues = [fileURL resourceValuesForKeys:resourceKeys error:&error];
// Skip directories and errors.
if (error || !resourceValues || [resourceValues[NSURLIsDirectoryKey] boolValue]) {
continue;
}
// Remove files that are older than the expiration date;
NSDate *modifiedDate = resourceValues[cacheContentDateKey];
if (expirationDate && [[modifiedDate laterDate:expirationDate] isEqualToDate:expirationDate]) {
[urlsToDelete addObject:fileURL];
continue;
}
// Store a reference to this file and account for its total size.
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize += totalAllocatedSize.unsignedIntegerValue;
cacheFiles[fileURL] = resourceValues;
}
for (NSURL *fileURL in urlsToDelete) {
[self.fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil];
}
// 第二轮清除:如果剩余文件的大小,仍然超过限制的磁盘缓存大小,那么执行第二轮清除
// 目标是将占用空间清除到最大限制的一半!
// 最“老”的文件最先被清除!
NSUInteger maxDiskSize = self.config.maxDiskSize;
if (maxDiskSize > 0 && currentCacheSize > maxDiskSize) {
// Target half of our maximum cache size for this cleanup pass.
const NSUInteger desiredCacheSize = maxDiskSize / 2;
// Sort the remaining cache files by their last modification time or last access time (oldest first).
NSArray<NSURL *> *sortedFiles = [cacheFiles keysSortedByValueWithOptions:NSSortConcurrent
usingComparator:^NSComparisonResult(id obj1, id obj2) {
return [obj1[cacheContentDateKey] compare:obj2[cacheContentDateKey]];
}];
// Delete files until we fall below our desired cache size.
for (NSURL *fileURL in sortedFiles) {
if ([self.fileManager removeItemAtURL:fileURL error:nil]) {
NSDictionary<NSString *, id> *resourceValues = cacheFiles[fileURL];
NSNumber *totalAllocatedSize = resourceValues[NSURLTotalFileAllocatedSizeKey];
currentCacheSize -= totalAllocatedSize.unsignedIntegerValue;
if (currentCacheSize < desiredCacheSize) {
break;
}
}
}
}
}
如何将缓存的 key 转换为文件名
static inline NSString * _Nonnull SDDiskCacheFileNameForKey(NSString * _Nullable key) {
const char *str = key.UTF8String;
if (str == NULL) {
str = "";
}
// 回顾加密哈希函数知识,将任意长度字符串,映射到固定长度的字符串,且不同的内容一定有不同的产出。
// C 语言中的字符数组,即字符串
// 将任意长度的 key,映射到 16 位长度的字符串!
unsigned char r[CC_MD5_DIGEST_LENGTH]; // 16
// @param1: 需要哈希的内容
// @param2: 内容的长度
// @param3: 存放产出的字符串
CC_MD5(str, (CC_LONG)strlen(str), r);
// 决定文件的扩展名,如果扩展名过长则舍弃!
NSURL *keyURL = [NSURL URLWithString:key];
NSString *ext = keyURL ? keyURL.pathExtension : key.pathExtension;
// File system has file name length limit, we need to check if ext is too long, we don't add it to the filename
if (ext.length > SD_MAX_FILE_EXTENSION_LENGTH) {
ext = nil;
}
// x 表示以十六进制形式输出
// 02 表示不足两位,前面补 0 输出;
// printf("%02X", 0x123); // 打�印出:123
// printf("%02X", 0x1); // 打印出:01
// 将字符串的每一位以 16 进制数输出!
NSString *filename = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%02x%@",
r[0], r[1], r[2], r[3], r[4], r[5], r[6], r[7], r[8], r[9], r[10],
r[11], r[12], r[13], r[14], r[15], ext.length == 0 ? @"" : [NSString stringWithFormat:@".%@", ext]];
return filename;
}
ExtendedCacheData
在阅读 SDDiskCache 的源码实现中,还发现了 extendedData 的读写,这是一个什么数据呢?
在 UIImage+ExtendedCacheData 中提到:Read and Write the extended object and bind it to the image. Which can hold some extra metadata like Image's scale factor, URL rich link, date, etc. The extended object should conforms to NSCoding, which we use NSKeyedArchiver and NSKeyedUnarchiver to archive it to data, and write to disk cache.
是外部可以自定义的一个遵循 NSCoding 协议的对象。当设置了它后,缓存时会使用 SDFileAttributeHelper 工具类,将其写入到文件属性中。
// 入参 name 是 static NSString * const SDDiskCacheExtendedAttributeName = @"com.hackemist.SDDiskCache";
// 这个属性名是 SDWebImage 定义的!
+ (NSData *)extendedAttribute:(NSString *)name atPath:(NSString *)path traverseLink:(BOOL)follow error:(NSError **)err {
// #define XATTR_NOFOLLOW 0x0001 /* Don't follow symbolic links */
// Symbolic Links 符号链接:是一个指向其他地方某个文件的指针,即快捷方式!
int flags = follow ? 0 : XATTR_NOFOLLOW;
// ssize_t getxattr(const char *path, const char *name, void *value, size_t size, u_int32_t position, int options);
// get length
// 读取位于 "path" 的文件的 "name" 属性长度!
ssize_t attrLen = getxattr([path fileSystemRepresentation], [name UTF8String], NULL, 0, 0, flags);
// get attribute data
NSMutableData *attrData = [NSMutableData dataWithLength:attrLen];
// 获取到的属性写入在 [attrData mutableBytes] 这块内存中并返回给调用者!
getxattr([path fileSystemRepresentation], [name UTF8String], [attrData mutableBytes], attrLen, 0, flags);
return attrData;
}
WWDC 2018 - Image and Graphics Best Practices
在开始探索图片如何解码前,我们先学习一些准备知识。
UIImageView is the class that UIKit provides for displaying a UIImage. In classical MVC style UIImage can be thought of as a model object, and UIImageView, of course, is a view.
UIImage is responsible for loading image content. And UIImageView is responsible for displaying it, for rendering it. In addition to rendering, being a continuous process, rather than a one-time event, there's this hidden phase called decoding.
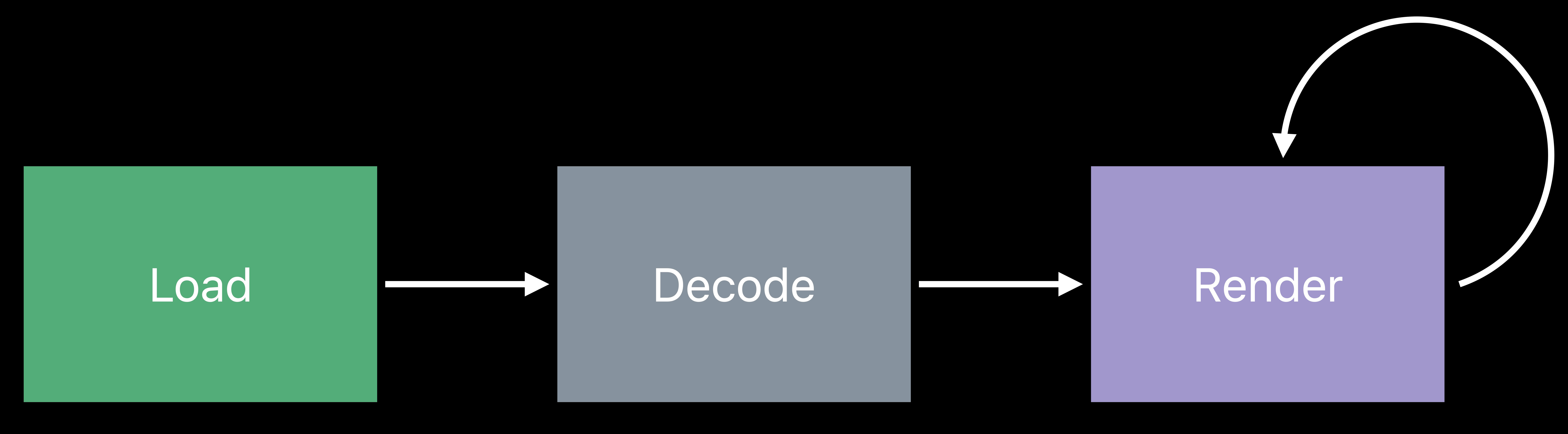
But in order to discuss decoding, I first need to discuss a concept called a buffer.
A buffer is just a contiguous region of memory. But we tend to use the term buffer when we're discussing memory that's composed of a sequence of elements of the same size, usually, of the same internal construction.
A data buffer, which is just a buffer that contains a sequence of bytes. A data buffer that contains an image file, typically, begins with some metadata describing the size of the image, and then, the image data itself, which is encoded in some form like JPEG compression or PNG.
The image buffer, a term we use for buffer that holds the in-memory representation of some image. Each element of this buffer describes the color and transparency of a single pixel in our image.
The frame buffer is what holds the actual rendered output of your application. As your application updates its view hierarchy UIKit will render the application's window and all of its subviews into the frame buffer. And that frame buffer provides per pixel color information that the display hardware will read in order to illuminate the pixels on the display, at a fixed interval like 60 fps.
When we've assigned a UIImage to this image view, in order to populate the frame buffer with per pixel data, UIImage will allocate an image buffer and performs an operation called decoding that will convert the JPEG or PNG or other encoded image data into per pixel image information.
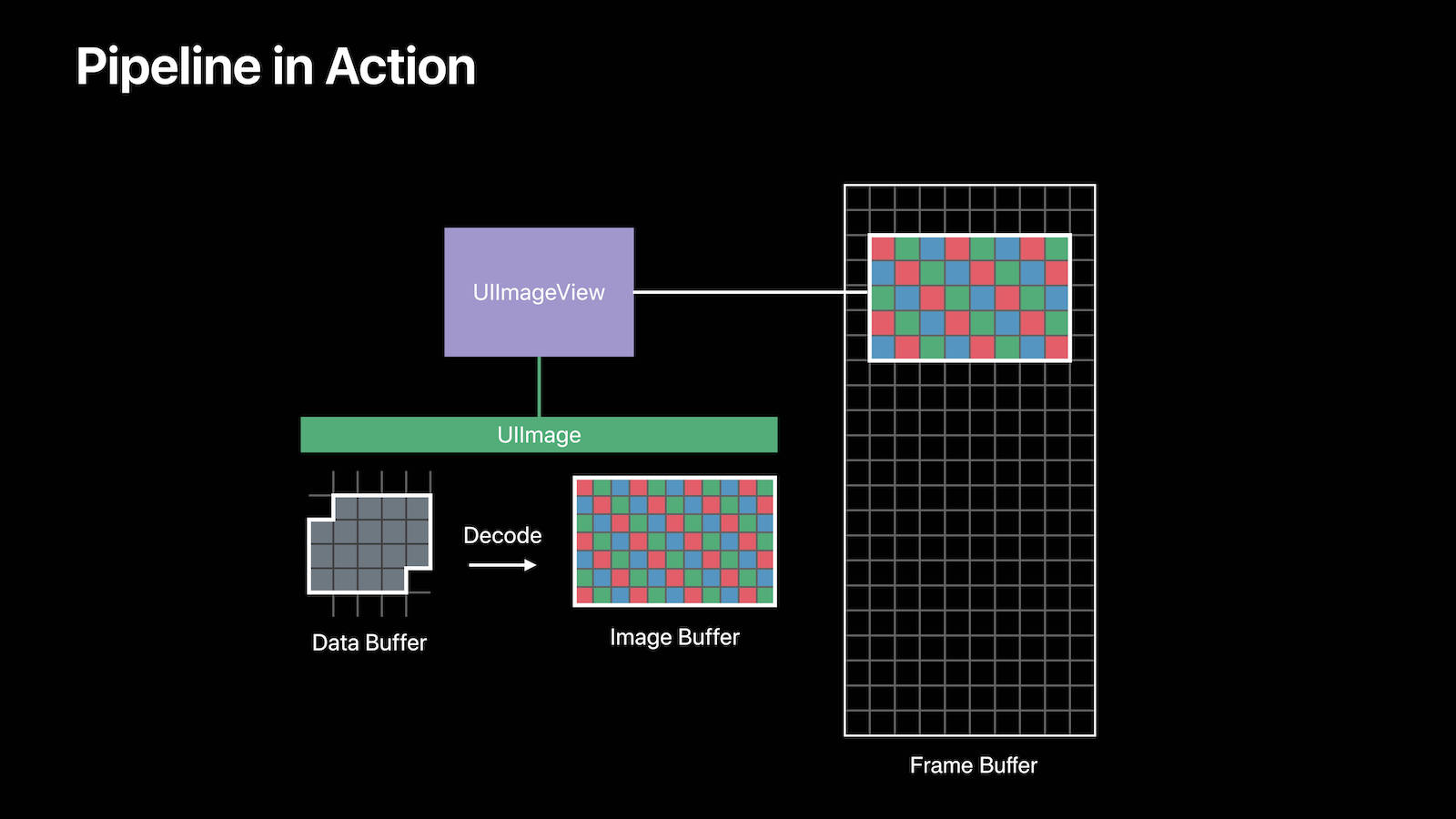
And then, depending on the content mode of our image view, when UIKit asks the image view to render, it will copy and scale the image data from the image buffer as it copies it into the frame buffer. 注意,缩放发生在 image buffer 拷贝到 frame buffer 的过程中!意味着,如果实际显示尺寸比原图尺寸小的话,decode 原图尺寸到 image buffer 然后再由 UIKit 缩放并拷贝到 frame buffer 是会浪费内存空间的!那么有没有办法在解码阶段只生成实际显示尺寸的 image buffer 呢?
Suppose the image view is actually smaller than the image we're going to display inside of it. Normally, the core animation framework would be responsible for shrinking that image down during the rendering phase, but we can save some memory by using downsampling technique. By capturing that shrinking operation into an object called the thumbnail, we're going to have a smaller decoded image buffer.
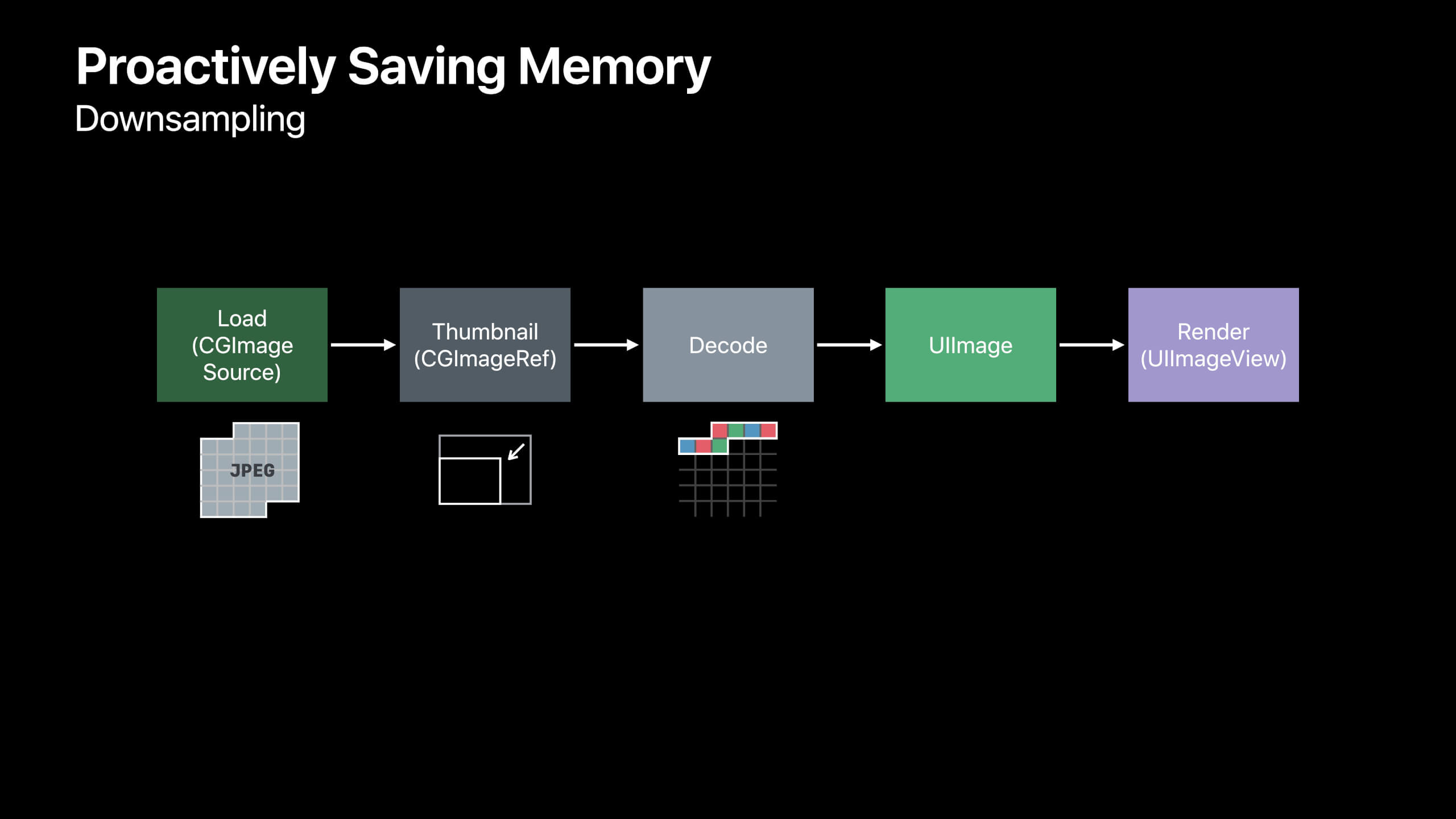
// Downsampling large images for display at smaller size
func downsample(imageAt imageURL: URL, to pointSize: CGSize, scale: CGFloat) -> UIImage {
// kCGImageSourceShouldCache Specifies whether the image should be cached in a decoded form.
// kCGImageSourceShouldCache = false tells the Core Graphics that we're just creating an object to represent the information stored in the file at this URL.
// Don't go ahead and decode this image immediately.
let imageSourceOptions = [kCGImageSourceShouldCache: false] as CFDictionary
let imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithURL(imageURL as CFURL, imageSourceOptions)!
let maxDimensionInPixels = max(pointSize.width, pointSize.height) * scale
// kCGImageSourceShouldCacheImmediately = true tells Core Graphics that when I ask you to create the thumbnail that's the exact moment you should create the decoded image buffer for me.
// The default value is kCFBooleanFalse (image decoding will happen at rendering time).
let downsampleOptions =
[kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageAlways: true,
kCGImageSourceShouldCacheImmediately: true,
kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform: true,
kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize: maxDimensionInPixels] as CFDictionary
let downsampledImage =
CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex(imageSource, 0, downsampleOptions)!
return UIImage(cgImage: downsampledImage)
}
- (UIImage *)downSampleImageAtPath:(NSString *)path toPointSize:(CGSize)pointSize scale:(CGFloat)scale {
// 加载图片的选项
CFStringRef key[1];
key[0] = kCGImageSourceShouldCache;
CFTypeRef value[1];
value[0] = (CFTypeRef)kCFBooleanFalse;
CFDictionaryRef imageOptions = CFDictionaryCreate(NULL,
(const void **) key,
(const void **) value,
1,
&kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks,
&kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
NSURL *fileURL = [NSURL fileURLWithPath:path];
CGImageSourceRef imageSource = CGImageSourceCreateWithURL((__bridge CFURLRef)fileURL, imageOptions);
// 降采样的选项
CFMutableDictionaryRef downSampleOptions = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(NULL,
4,
&kCFTypeDictionaryKeyCallBacks,
&kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
CGFloat maxDimensionInPixels = MAX(pointSize.width, pointSize.height) * scale;
NSNumber *maxDimensionInPixelsNum = [NSNumber numberWithFloat:maxDimensionInPixels];
CFDictionaryAddValue(downSampleOptions, kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageAlways, kCFBooleanTrue);
CFDictionaryAddValue(downSampleOptions, kCGImageSourceShouldCacheImmediately, kCFBooleanTrue);
CFDictionaryAddValue(downSampleOptions, kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform, kCFBooleanTrue);
CFDictionaryAddValue(downSampleOptions, kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize, (__bridge CFNumberRef)maxDimensionInPixelsNum);
// 创建降采样图片
CGImageRef imageRef = CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex(imageSource, 0, downSampleOptions);
return [UIImage imageWithCGImage:imageRef];
}
Best practices when implementing UICollectionView:
- Prefetching allows CollectionView to inform our data source that it needs a cell right in the very near future.
- Performing decoding in the background. Rather than simply dispatching work to one of the global asynchronous queues, we're going to create a serial queue to avoid thread explosion. (GCD is keep creating new threads and spend a lot of time moving between those threads to try to make incremental progress)
let serialQueue = DispatchQueue(label: "Decode queue")
func collectionView(_ collectionView: UICollectionView, prefetchItemsAt indexPaths: [IndexPath]) {
// Asynchronously decode and downsample every image we are about to show
for indexPath in indexPaths {
serialQueue.async {
let downsampledImage = downsample(images[indexPath.row])
DispatchQueue.main.async {
self.update(at: indexPath, with: downsampledImage)
}
}
}
}
SDImageCacheDecodeImageData
从一段最简单的加载图片代码说起:
let image = UIImage(named: "unnamed") // encoded image in data buffer
imageView.image = image; // decoded image in image buffer
创建一个 UIImage 实例只会加载 data buffer, 将图像显示到屏幕上才会触发解码,可以通过 Xcode 断点调试,观察内存占用情况来验证这一点。解码后的数据即 image buffer,包含了图像所有像素的信息,会占用较多的内存。
By default, we will decode the image in the background during cache query and download from the network. This can help to improve performance because when rendering image on the screen, it need to be firstly decoded. But this happen on the main queue by Core Animation. However, this process may increase the memory usage as well. 默认情况下,将图片渲染在屏幕上,需要先由 Core Animation 在主线程进行解码。SDWebImage 在查询缓存和下载图片时帮我们在后台线程进行解码,这可以提高性能,但会增加内存占用(例如你并不实际显示这张图片)。
UIImage * _Nullable SDImageCacheDecodeImageData(NSData * _Nonnull imageData, NSString * _Nonnull cacheKey, SDWebImageOptions options, SDWebImageContext * _Nullable context) {
UIImage *image; // 最终返回的图片
// 这里省略对动图的处理相关代码!
// 如果是 UIKit,则需考虑 UIScreen.main.scale!
// 看 cacheKey 中是否含有 @2x @3x,有的话,取出来作为 scaleFactor!
NSNumber *scaleValue = context[SDWebImageContextImageScaleFactor];
CGFloat scale = scaleValue.doubleValue >= 1 ? scaleValue.doubleValue : SDImageScaleFactorForKey(cacheKey);
// 缩放是否需保持原始宽高比例!
NSNumber *preserveAspectRatioValue = context[SDWebImageContextImagePreserveAspectRatio];
// 缩略图大小
NSValue *thumbnailSizeValue;
// 是否需要降采样!
BOOL shouldScaleDown = SD_OPTIONS_CONTAINS(options, SDWebImageScaleDownLargeImages);
if (shouldScaleDown) {
// 注意了!!
// 每一个像素需要存储 RGBA 信息,共 8 bits * 4 = 4 bytes!
// defaultScaleDownLimitBytes defines the maximum size in MB of the decoded image
// 这个变量定义了解码后的图片所占用的最大内存大小,对于 UIKit,SDWebImage 给的建议值是 60MB!
// 计算出图片像素点的个数!
CGFloat thumbnailPixels = SDImageCoderHelper.defaultScaleDownLimitBytes / 4;
// 根据内存限制所计算出的缩略图宽高!UIKit 计算出来大概是宽高各 3965.9!
CGFloat dimension = ceil(sqrt(thumbnailPixels));
thumbnailSizeValue = @(CGSizeMake(dimension, dimension));
}
if (context[SDWebImageContextImageThumbnailPixelSize]) {
thumbnailSizeValue = context[SDWebImageContextImageThumbnailPixelSize];
}
if (!image) {
// 见 SDImageCodersManager
// 默认调用 SDImageIOCoder 的方法!
image = [imageCoder decodedImageWithData:imageData options:coderOptions];
}
if (image) {
BOOL shouldDecode = !SD_OPTIONS_CONTAINS(options, SDWebImageAvoidDecodeImage);
if (shouldDecode) {
image = [SDImageCoderHelper decodedImageWithImage:image];
}
}
return image;
}
接下来我们看 SDImageIOCoder 和 SDImageCoderHelper 的 decode 分别做了什么!
SDImageIOCoder
- (UIImage *)decodedImageWithData:(NSData *)data options:(nullable SDImageCoderOptions *)options {
CGImageSourceRef source = CGImageSourceCreateWithData((__bridge CFDataRef)data, NULL);
CGSize thumbnailSize = CGSizeZero;
NSValue *thumbnailSizeValue = options[SDImageCoderDecodeThumbnailPixelSize];
thumbnailSize = thumbnailSizeValue.CGSizeValue; // in pixels
UIImage *image = [SDImageIOAnimatedCoder createFrameAtIndex:0 source:source scale:scale preserveAspectRatio:preserveAspectRatio thumbnailSize:thumbnailSize options:nil];
CFRelease(source);
return image;
}
再看到 SDImageIOAnimatedCoder:
+ (UIImage *)createFrameAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index source:(CGImageSourceRef)source scale:(CGFloat)scale preserveAspectRatio:(BOOL)preserveAspectRatio thumbnailSize:(CGSize)thumbnailSize options:(NSDictionary *)options {
// Parse the image properties
NSDictionary *properties = (__bridge_transfer NSDictionary *)CGImageSourceCopyPropertiesAtIndex(source, index, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)options);
NSUInteger pixelWidth = [properties[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImagePropertyPixelWidth] unsignedIntegerValue];
NSUInteger pixelHeight = [properties[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImagePropertyPixelHeight] unsignedIntegerValue];
CGImagePropertyOrientation exifOrientation = (CGImagePropertyOrientation)[properties[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImagePropertyOrientation] unsignedIntegerValue];
if (!exifOrientation) {
exifOrientation = kCGImagePropertyOrientationUp;
}
// 见 https://developer.apple.com/documentation/uniformtypeidentifiers/uttype
CFStringRef uttype = CGImageSourceGetType(source);
CGImageRef imageRef;
BOOL createFullImage = thumbnailSize.width == 0 || thumbnailSize.height == 0 || pixelWidth == 0 || pixelHeight == 0 || (pixelWidth <= thumbnailSize.width && pixelHeight <= thumbnailSize.height);
if (createFullImage) {
// 不需要降采样,创建原图!
imageRef = CGImageSourceCreateImageAtIndex(source, index, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)[decodingOptions copy]);
} else {
// 需要降采样,创建缩略图!
decodingOptions[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform] = @(preserveAspectRatio);
// Resizing is accomplished by the kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize option, which specifies the maximum dimension used to scale the image at its original aspect ratio.
CGFloat maxPixelSize;
if (preserveAspectRatio) {
CGFloat pixelRatio = pixelWidth / pixelHeight;
CGFloat thumbnailRatio = thumbnailSize.width / thumbnailSize.height;
if (pixelRatio > thumbnailRatio) {
maxPixelSize = thumbnailSize.width;
} else {
maxPixelSize = thumbnailSize.height;
}
} else {
maxPixelSize = MAX(thumbnailSize.width, thumbnailSize.height);
}
decodingOptions[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImageSourceThumbnailMaxPixelSize] = @(maxPixelSize);
decodingOptions[(__bridge NSString *)kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailFromImageAlways] = @(YES);
imageRef = CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex(source, index, (__bridge CFDictionaryRef)[decodingOptions copy]);
}
if (!imageRef) {
return nil;
}
// Thumbnail image post-process
if (!createFullImage) {
if (preserveAspectRatio) {
// kCGImageSourceCreateThumbnailWithTransform will apply EXIF transform as well, we should not apply twice
exifOrientation = kCGImagePropertyOrientationUp;
} else {
// `CGImageSourceCreateThumbnailAtIndex` take only pixel dimension, if not `preserveAspectRatio`, we should manual scale to the target size
// 入参 thumbnailSize 的宽高比例不一定和原图一样的!
// 前面创建好的缩略图是根据 thumbnailSize 宽、高的较大值创建,保持了原图的比例的!
// 此处还需要进行再次缩放以得到 thumbnailSize 的图片!
CGImageRef scaledImageRef = [SDImageCoderHelper CGImageCreateScaled:imageRef size:thumbnailSize];
CGImageRelease(imageRef);
imageRef = scaledImageRef;
}
}
UIImageOrientation imageOrientation = [SDImageCoderHelper imageOrientationFromEXIFOrientation:exifOrientation];
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:imageRef scale:scale orientation:imageOrientation];
CGImageRelease(imageRef);
return image;
}
SDImageCoderHelper
+ (UIImage *)decodedImageWithImage:(UIImage *)image {
CGImageRef imageRef = [self CGImageCreateDecoded:image.CGImage];
UIImage *decodedImage = [[UIImage alloc] initWithCGImage:imageRef scale:image.scale orientation:image.imageOrientation];
return decodedImage;
}
+ (CGImageRef)CGImageCreateDecoded:(CGImageRef)cgImage orientation:(CGImagePropertyOrientation)orientation {
size_t width = CGImageGetWidth(cgImage);
size_t height = CGImageGetHeight(cgImage);
BOOL hasAlpha = [self CGImageContainsAlpha:cgImage];
CGBitmapInfo bitmapInfo = kCGBitmapByteOrder32Host;
bitmapInfo |= hasAlpha ? kCGImageAlphaPremultipliedFirst : kCGImageAlphaNoneSkipFirst;
/* 创建上下文
@param0 data
@param1 width
@param2 height
@param3 bitsPerComponent
@param4 bytesPerRow
@param5 space
@param6 bitmapInfo
The context draws into a bitmap which is `width' pixels wide and `height' pixels high.
The number of components for each pixel is specified by `space',
which may also specify a destination color profile.
Note that the only legal case when `space' can be NULL is when alpha is specified as kCGImageAlphaOnly.
The number of bits for each component of a pixel is specified by `bitsPerComponent'.
The number of bytes per pixel is equal to `(bitsPerComponent * number of components + 7)/8'.
Each row of the bitmap consists of `bytesPerRow' bytes, which must be at least
`width * bytes per pixel' bytes; in addition, `bytesPerRow' must be an
integer multiple of the number of bytes per pixel.
`data', if non-NULL, points to a block of memory at least `bytesPerRow * height' bytes.
If `data' is NULL, the data for context is allocated automatically and freed
when the context is deallocated.
`bitmapInfo' specifies whether the bitmap
should contain an alpha channel and how it's to be generated, along with
whether the components are floating-point or integer. */
CGContextRef context = CGBitmapContextCreate(NULL, newWidth, newHeight, 8, 0, [self colorSpaceGetDeviceRGB], bitmapInfo);
// 解码到 image buffer!!
// 实际就是对图片进行重新绘制,得到一张新的解压缩后的位图!!
// 绘图!!
/* Return an image containing a snapshot of the bitmap context `context'. */
CGImageRef newImageRef = CGBitmapContextCreateImage(context);
CGContextRelease(context);
return newImageRef;
}
图片解码研究完了,缓存的全流程探索完毕!
SDImageLoader
SDWebImageDownloader
SDWebImageDownloader 是 SDImageLoader 协议的默认实现。
@interface SDWebImageDownloadToken : NSObject <SDWebImageOperation>: A token associated with each download. Can be used to cancel a download.
NSURLSessionTaskMetrics: Each NSURLSessionTaskMetrics object contains the taskInterval and redirectCount, as well as metrics for each request-and-response transaction made during the execution of the task.
这里设置了两个默认的 HTTP Header,有关 HTTP Header 的说明可以在 RFC2616 找到。
// User-Agent Header; see http://www.w3.org/Protocols/rfc2616/rfc2616-sec14.html#sec14.43
// 输出 `demo/1.0 (iPhone; iOS 14.0; Scale/2.00)`
userAgent = [NSString stringWithFormat:@"%@/%@ (%@; iOS %@; Scale/%0.2f)",
[[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary][(__bridge NSString *)kCFBundleExecutableKey] ?: [[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary][(__bridge NSString *)kCFBundleIdentifierKey], [[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary][@"CFBundleShortVersionString"] ?: [[NSBundle mainBundle] infoDictionary][(__bridge NSString *)kCFBundleVersionKey],
[[UIDevice currentDevice] model],
[[UIDevice currentDevice] systemVersion],
[[UIScreen mainScreen] scale]];
headerDictionary[@"User-Agent"] = userAgent;
headerDictionary[@"Accept"] = @"image/*,*/*;q=0.8"; // 图片类型权重 1.0;任意类型权重 0.8;即优先返回图片类型
我们知道 SDWebImageCombinedOperation 包含了两个操作 cacheOperation 和 loaderOperation,其中 loaderOperation 就是从这里创建的:
- (id<SDWebImageOperation>)requestImageWithURL:(NSURL *)url options:(SDWebImageOptions)options context:(SDWebImageContext *)context progress:(SDImageLoaderProgressBlock)progressBlock completed:(SDImageLoaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock {
return [self downloadImageWithURL:url options:downloaderOptions context:context progress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
}
- (nullable SDWebImageDownloadToken *)downloadImageWithURL:(nullable NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context
progress:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock)progressBlock
completed:(nullable SDWebImageDownloaderCompletedBlock)completedBlock {
SD_LOCK(self.operationsLock);
id downloadOperationCancelToken;
NSOperation<SDWebImageDownloaderOperation> *operation = [self.URLOperations objectForKey:url];
if (!operation || operation.isFinished || operation.isCancelled) {
operation = [self createDownloaderOperationWithUrl:url options:options context:context];
@weakify(self);
operation.completionBlock = ^{
@strongify(self);
if (!self) {
return;
}
SD_LOCK(self.operationsLock);
[self.URLOperations removeObjectForKey:url];
SD_UNLOCK(self.operationsLock);
};
self.URLOperations[url] = operation;
downloadOperationCancelToken = [operation addHandlersForProgress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
[self.downloadQueue addOperation:operation];
} else {
// When we reuse the download operation to attach more callbacks, there may be thread safe issue because the getter of callbacks may in another queue (decoding queue or delegate queue)
// So we lock the operation here, and in `SDWebImageDownloaderOperation`, we use `@synchonzied (self)`, to ensure the thread safe between these two classes.
@synchronized (operation) {
downloadOperationCancelToken = [operation addHandlersForProgress:progressBlock completed:completedBlock];
}
}
SD_UNLOCK(self.operationsLock);
SDWebImageDownloadToken *token = [[SDWebImageDownloadToken alloc] initWithDownloadOperation:operation];
token.url = url;
token.request = operation.request;
token.downloadOperationCancelToken = downloadOperationCancelToken;
return token;
}
- (nullable NSOperation<SDWebImageDownloaderOperation> *)createDownloaderOperationWithUrl:(nonnull NSURL *)url
options:(SDWebImageDownloaderOptions)options
context:(nullable SDWebImageContext *)context {
// In order to prevent from potential duplicate caching (NSURLCache + SDImageCache) we disable the cache for image requests if told otherwise
// 已经做了图片缓存了,默认忽略 NSURLSession 的缓存!
NSURLRequestCachePolicy cachePolicy = options & SDWebImageDownloaderUseNSURLCache ? NSURLRequestUseProtocolCachePolicy : NSURLRequestReloadIgnoringLocalCacheData;
NSMutableURLRequest *mutableRequest = [[NSMutableURLRequest alloc] initWithURL:url cachePolicy:cachePolicy timeoutInterval:timeoutInterval];
mutableRequest.HTTPShouldHandleCookies = SD_OPTIONS_CONTAINS(options, SDWebImageDownloaderHandleCookies);
mutableRequest.HTTPShouldUsePipelining = YES;
SD_LOCK(self.HTTPHeadersLock);
mutableRequest.allHTTPHeaderFields = self.HTTPHeaders;
SD_UNLOCK(self.HTTPHeadersLock);
// 调用协议的方法
NSOperation<SDWebImageDownloaderOperation> *operation = [[operationClass alloc] initWithRequest:request inSession:self.session options:options context:context];
if (self.config.executionOrder == SDWebImageDownloaderLIFOExecutionOrder) {
// Emulate LIFO execution order by systematically, each previous adding operation can dependency the new operation
// This can gurantee the new operation to be execulated firstly, even if when some operations finished, meanwhile you appending new operations
// Just make last added operation dependents new operation can not solve this problem. See test case #test15DownloaderLIFOExecutionOrder
for (NSOperation *pendingOperation in self.downloadQueue.operations) {
[pendingOperation addDependency:operation];
}
}
return operation;
}
NSOperation
在开始研究 SDWebImageDownloaderOperation 前,先复习一下 NSOperation 的 start 和 main 两个方法。
当 main 方法返回后,operation 就结束了。当我们在 main 方法中有异步操作时,这可能不是我们想要的结果。比如以下这段代码,operation 已经完成了,网络请求才返回。
private final class DownloadOperation: Operation {
override func main() {
let url = URL(string: "https://www.baidu.com/")!
let request = URLRequest(url: url)
let dataTask = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { (data, response, error) in
print("URL data task completed")
}
dataTask.resume()
}
}
let op = DownloadOperation()
operationQueue.addOperation(op)
DispatchQueue.main.asyncAfter(deadline: .now() + 0.001) {
print("operation finished: \(op.isFinished)")
}
因此,如果等待异步方法执行完后再完成操作,可以重写 start 方法。注意,当我们重写 start 方法时,需要自行追踪 operation 的状态并实现状态转换;并且,还需要调用 KVO 方法通知外部!
private final class DownloadOperation: Operation {
private var _executing: Bool = false
override var isExecuting: Bool {
get {
return _executing
}
set {
if _executing != newValue {
willChangeValue(forKey: "isExecuting")
_executing = newValue
didChangeValue(forKey: "isExecuting")
}
}
}
private var _finished: Bool = false
override var isFinished: Bool {
get {
return _finished
}
set {
if _finished != newValue {
willChangeValue(forKey: "isFinished")
_finished = newValue
didChangeValue(forKey: "isFinished")
}
}
}
override func start() {
self.isExecuting = true
let url = URL(string: "https://www.baidu.com")!
let request = URLRequest(url: url)
let dataTask = URLSession.shared.dataTask(with: request) { (data, response, error) in
print("URL data task completed")
self.isExecuting = false
self.isFinished = true
}
dataTask.resume()
}
}
let op = DownloadOperation()
operationQueue.addOperation(op)
SDWebImageDownloaderOperation
了解了 NSOperation 的知识后,我们来看 SDWebImageDownloaderOperation 的相关方法
- (void)start {
@synchronized (self) {
if (self.isCancelled) {
self.finished = YES;
// Operation cancelled by user before sending the request
[self callCompletionBlocksWithError:[NSError errorWithDomain:SDWebImageErrorDomain code:SDWebImageErrorCancelled userInfo:@{NSLocalizedDescriptionKey : @"Operation cancelled by user before sending the request"}]];
[self reset];
return;
}
// 启动后台任务,申请 App 退出后台后额外的执行时间
Class UIApplicationClass = NSClassFromString(@"UIApplication");
BOOL hasApplication = UIApplicationClass && [UIApplicationClass respondsToSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
if (hasApplication && [self shouldContinueWhenAppEntersBackground]) {
__weak typeof(self) wself = self;
UIApplication * app = [UIApplicationClass performSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
self.backgroundTaskId = [app beginBackgroundTaskWithExpirationHandler:^{
[wself cancel];
}];
}
// session 一般情况下是从 SDWebImageDownloader 传进来的
NSURLSession *session = self.unownedSession;
if (!session) {
NSURLSessionConfiguration *sessionConfig = [NSURLSessionConfiguration defaultSessionConfiguration];
sessionConfig.timeoutIntervalForRequest = 15;
session = [NSURLSession sessionWithConfiguration:sessionConfig
delegate:self
delegateQueue:nil];
self.ownedSession = session;
}
self.dataTask = [session dataTaskWithRequest:self.request];
self.executing = YES;
}
if (self.dataTask) {
[self.dataTask resume];
for (SDWebImageDownloaderProgressBlock progressBlock in [self callbacksForKey:kProgressCallbackKey]) {
progressBlock(0, NSURLResponseUnknownLength, self.request.URL);
}
__block typeof(self) strongSelf = self;
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:SDWebImageDownloadStartNotification object:strongSelf];
});
}
}
- (void)cancel {
@synchronized (self) {
[self cancelInternal];
}
}
- (void)cancelInternal {
if (self.isFinished) return;
[super cancel];
if (self.dataTask) {
[self.dataTask cancel];
__block typeof(self) strongSelf = self;
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:SDWebImageDownloadStopNotification object:strongSelf];
});
if (self.isExecuting) self.executing = NO;
if (!self.isFinished) self.finished = YES;
}
[self reset];
}
- (void)reset {
@synchronized (self) {
[self.callbackBlocks removeAllObjects];
self.dataTask = nil;
if (self.ownedSession) {
[self.ownedSession invalidateAndCancel];
self.ownedSession = nil;
}
if (self.backgroundTaskId != UIBackgroundTaskInvalid) {
// If backgroundTaskId != UIBackgroundTaskInvalid, sharedApplication is always exist
UIApplication * app = [UIApplication performSelector:@selector(sharedApplication)];
[app endBackgroundTask:self.backgroundTaskId];
self.backgroundTaskId = UIBackgroundTaskInvalid;
}
}
}
接下来看对 NSURLSessionDelegate 相关方法的实现,重点关注下载完成后,解码的过程
- (void)URLSession:(NSURLSession *)session task:(NSURLSessionTask *)task didCompleteWithError:(NSError *)error {
if (self.isFinished) return;
@synchronized(self) {
self.dataTask = nil;
__block typeof(self) strongSelf = self;
dispatch_async(dispatch_get_main_queue(), ^{
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:SDWebImageDownloadStopNotification object:strongSelf];
if (!error) {
[[NSNotificationCenter defaultCenter] postNotificationName:SDWebImageDownloadFinishNotification object:strongSelf];
}
});
}
// make sure to call `[self done]` to mark operation as finished
if (error) {
// custom error instead of URLSession error
if (self.responseError) {
error = self.responseError;
}
[self callCompletionBlocksWithError:error];
[self done];
} else {
NSData *imageData = [self.imageData copy];
self.imageData = nil;
// decode the image in coder queue, cancel all previous decoding process
[self.coderQueue cancelAllOperations];
[self.coderQueue addOperationWithBlock:^{
UIImage *image = SDImageLoaderDecodeImageData(imageData, self.request.URL, [[self class] imageOptionsFromDownloaderOptions:self.options], self.context);
[self callCompletionBlocksWithImage:image imageData:imageData error:nil finished:YES];
[self done];
}];
}
}
SDAnimatedImage
5.0 版本开始,抛弃了 FLAnimatedImage,由框架自行实现。SDAnimatedImage 继承自 UIImage,与 SDAnimatedImageView 配合使用展示动图。
SDAnimatedImageView, by default, will decode and cache the image frames with a buffer (where the buffer size is calculated based on current memory status), when the buffer is out of limit size, the older image frame will be purged to free up memory. This allows you to keep a balance in both CPU & memory.
SDWebImagePrefetcher
使用:
let prefetchURLs = [URL]()
SDWebImagePrefetcher.shared.prefetchURLs(prefetchURLs)