设计题
有限状态机
有限状态自动机(FSM "Finite State Machine" 或者 FSA "Finite State Automaton")解决一个输入序列,经过 FSM,最终停留在什么状态这样一个问题。构建 FSM 产出这样一个字典:在 x 状态下,输入 a,就会得到 y 状态。
8-字符串转换整数(atoi)
将字符串转换成整数。"42"、" -42"、"4193 with words"、"words and 987"、"-91283472332"……
每一位的字符,可能有 4 种情况:数字、+/-号、字母、空格。再加上考虑边界情况的处理,如果用 if...else... 结构,代码会写得比较臃肿。因此考虑用有限状态机。
class Automator {
public:
Automator() {
um["start"] = {"start", "sign", "number", "end"};
um["sign"] = {"end", "end", "number", "end"};
um["number"] = {"end", "end", "number", "end"};
um["end"] = {"end", "end", "end", "end"};
}
int columnOf(char input) {
if (isspace(input)) {
return 0;
} else if (input == '+' || input == '-') {
return 1;
} else if (isdigit(input)) {
return 2;
} else {
return 3;
}
}
void input(char c) {
state = um[state][columnOf(c)];
if (state == "number") {
res = res * 10 + (c - '0');
res = sign == 1 ? min(res, (long long)INT_MAX) : min(res, -(long long)INT_MIN);
} else if (state == "sign") {
sign = c == '+' ? 1 : -1;
}
}
string state = "start"; // 当前状态
int sign = 1; // 正负号
long long res = 0; // 结果
private:
unordered_map<string, vector<string>> um; // 数组 0,1,2,3 分别代表空格、符号、数字、字符
};
class Solution {
public:
int myAtoi(string s) {
Automator autom = Automator();
for (char c : s) {
autom.input(c);
if (autom.state == "end") {
break;
}
}
int res = static_cast<int>(autom.sign * autom.res);
return res;
}
};
65-有效数字
393-UTF-8 编码验证
数据结构
146-LRU Cache
设计一个 LRU 缓存容器,支持以下接口:
LRUCache(int capacity) 初始化时传入容器的容量。
int get(int key) 如果 key 存在于容器中则返回 value,否则返回 -1。
void put(int key, int value) 如果 key 存在则更新其 value;否则插入键值对。当超出容量时,移除最久未使用的值。
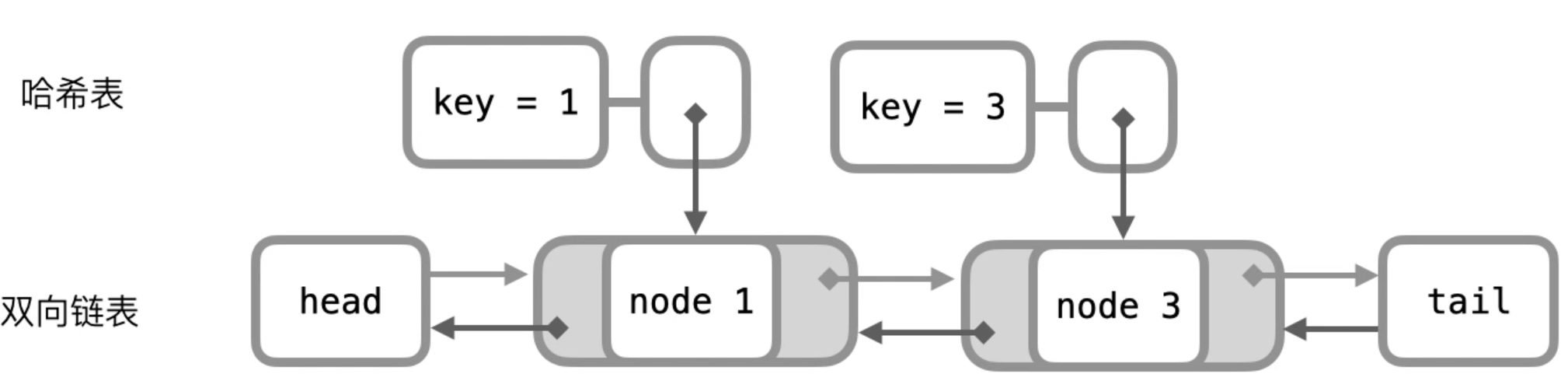
实现本题的两种操作,需要用到一个哈希表和一个双向链表。
哈希表存储键到双向链表中的节点的映射。
链表要存储头节点;双向链表要存储头、尾两个节点。靠近头部的键值对是最近使用的,靠近尾部的键值对是最久未使用的。
#include <unordered_map>
using std::unordered_map;
#include <memory>
using std::shared_ptr;
using std::make_shared;
struct Node {
Node(int k, int v) : key(k), val(v) {}
int key;
int val;
shared_ptr<Node> pre = nullptr;
shared_ptr<Node> next = nullptr;
};
class LRUCache {
public:
LRUCache(int capacity) : capacity(capacity) {
// 伪头部和尾部节点,不实际存储键值对
head->next = tail;
tail->pre = head;
}
int get(int key) {
if (um.find(key) != um.end()) {
shared_ptr<Node> node = um[key];
moveToHead(node);
return node->val;
} else {
return -1;
}
}
void put(int key, int value) {
if (um.find(key) != um.end()) {
shared_ptr<Node> node = um[key];
node->val = value;
moveToHead(node);
} else {
shared_ptr<Node> node = make_shared<Node>(key, value);
um[key] = node;
addToHead(node);
++size;
if (size > capacity) {
shared_ptr<Node> tail = removeTail();
um.erase(tail->key);
--size;
}
}
}
private:
int capacity; // 容量
int size = 0; // 容器当前大小
unordered_map<int, shared_ptr<Node>> um; // key -> 节点
shared_ptr<Node> head = make_shared<Node>(0, 0); // 头部是最近使用的
shared_ptr<Node> tail = make_shared<Node>(0, 0); // 尾部是最久未使用的
void moveToHead(shared_ptr<Node> node) {
removeNode(node);
addToHead(node);
}
void addToHead(shared_ptr<Node> node) {
node->pre = head;
node->next = head->next;
head->next->pre = node;
head->next = node;
}
void removeNode(shared_ptr<Node> node) {
node->next->pre = node->pre;
node->pre->next = node->next;
}
shared_ptr<Node> removeTail() {
shared_ptr<Node> tmp = tail->pre; // 注意,这才是真正的尾巴!
removeNode(tmp);
return tmp;
}
};
155-最小栈
设计一个支持 push, pop, top 操作,并能在常数时间内检索到最小元素的栈。
解决这个问题要用到一个辅助栈,每次 push 操作,将数压入普通栈、同时将当前最小值压入辅助栈,使他们同进同出、一一对应。
class MinStack {
public:
void push(int x) {
x_stack.push(x);
if (min_stack.empty()) {
min_stack.push(x);
} else {
min_stack.push(min(min_stack.top(), x));
}
}
void pop() {
x_stack.pop();
min_stack.pop();
}
int top() {
return x_stack.top();
}
int getMin() {
return min_stack.top();
}
private:
stack<int> x_stack;
stack<int> min_stack;
};
225-用队列实现栈
插入后,将队列的前 N 个元素依次出队并入队。插入操作是 O(N),其余是 O(1)。
class MyStack {
public:
void push(int x) {
int size = q.size();
q.push(x);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
q.push(q.front());
q.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int front = q.front();
q.pop();
return front;
}
int top() {
return q.front();
}
bool empty() {
return q.empty();
}
private:
queue<int> q;
};
232-用栈实现队列
class MyQueue {
public:
void push(int x) {
int size = stk1.size();
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
stk2.push(stk1.top());
stk1.pop();
}
stk1.push(x);
for (int i = 0; i < size; ++i) {
stk1.push(stk2.top());
stk2.pop();
}
}
int pop() {
int top = stk1.top();
stk1.pop();
return top;
}
int peek() {
return stk1.top();
}
bool empty() {
return stk1.empty();
}
private:
stack<int> stk1;
stack<int> stk2;
};
895-最大频率栈
这题使用到的数据结构比较巧妙,除了常规的数字到出现频次的字典;还需要一个频次到栈的字典。
class FreqStack {
public:
void push(int val) {
freq[val] += 1;
int f = freq[val];
maxFreq = max(f, maxFreq);
group[f].push(val);
}
int pop() {
int res = group[maxFreq].top();
group[maxFreq].pop();
if (group[maxFreq].empty()) {
maxFreq -= 1;
}
freq[res] -= 1;
return res;
}
private:
unordered_map<int, int> freq; // 数 -> 频次
unordered_map<int, stack<int>> group; // 频次 -> 该频次下的数
int maxFreq; // 当前最大频次
};
分析代码执行过程可以得知,频次是从 1 开始的连续数字,因此,group 这个字典也可以用数组代替。