加解密与数字签名
加解密
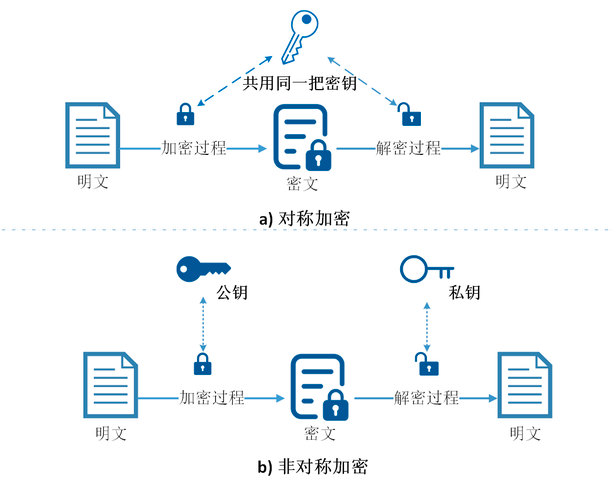
如果加密和解密过程的密钥相同,则称为对称加密,反之为非对称加密。
对称加密现在的标准 (SOTA):AES-GCM。具体算法:AES-128 或 AES-256。它属于 AEAD (Authenticated Encryption with Associated Data,带关联数据的认证加密)。这意味着它不仅加密数据(保密性),还同时验证数据的完整性(防篡改)。
RSA 的安全性建立在分解两个大素数乘积的的巨大难度之上。为确保足够安全,密钥长度需不断增大,计算开销剧增。RSA 根证书的普及度极高,目前全球大部分 SSL 证书依然是 RSA 签名的(RSA-2048 或 RSA-3072)。
ECC(椭圆曲线密码学,Elliptic Curve Cryptography)与 RSA(Rivest-Shamir-Adleman)是目前互联网最主流的两种非对称加密算法。虽然 RSA 历史更悠久,但 ECC 凭借其极高的效率正在逐渐成为主流(特别是在移动互联网和区块链领域)。比特币、以太坊、现代 HTTPS(TLS 1.3)均使用 ECC。RSA 3072 位才能达到的安全性,ECC 只需要 256 位。这极大地节省了存储空间和传输带宽。
ECDHE(Elliptic Curve Diffie-Hellman Ephemeral)是当前非对称加密中密钥交换的 SOTA 标准,是 TLS 1.3 协议的标配,用于在不安全的网络中让通信双方安全协商出一个后续用于大容量数据加密的对称密钥。它基于椭圆曲线密码学(ECC)实现,同时带有 Ephemeral 属性,每次通信会话都会生成全新的临时密钥对,而非重复使用固定密钥。且满足前向保密(PFS),即使后续服务器的主私钥被泄露,黑客记录了通信流量,也无法解密已发生的历史会话数据。因为每次会话的密钥由临时密钥协商生成,与主私钥无直接关联,从根本上降低了密钥泄露的影响范围。
加密哈希函数
哈希函数将任意长度的消息,映射到固定长度的哈希字符串。
加密哈希函数满足以下特性:对任意两个不同的消息,哈希值不一样。
SHA-256 的输入可以是任意长度的数据,从 1 个字节到数 GB 甚至更大。可能的输入数量是无限的。
SHA-256 的输出是一个固定长度的 256 位(32 字节)的哈希值。这意味着总共有 2^256 个可能的哈希值。
根据数学上的“鸽巢原理”,如果你有无限只“鸽子”(输入数据)要飞进有限个“鸽巢”(哈希值),那么必然有多个不同的输入会进入同一个鸽巢。这种两个不同的输入产生相同哈希值的现象,就叫做 “碰撞”。所以,从纯数学和逻辑上讲,碰撞是必然存在的。
但截至目前,世界上没有任何人(包括国家级的实验室、大型科技公司)公开宣布过通过计算找到了 SHA-256 的碰撞。这被认为是计算上不可行的。根据“生日攻击”:要找到一对随机碰撞,平均需要检查大约 2^128 个输入,即使全世界的计算机从宇宙诞生(约 138 亿年)算起直到现在,所尝试的计算次数也远远小于 2^128。
生日攻击 是一种利用“生日悖论”概率原理,来寻找哈希函数碰撞的通用方法。它的核心在于:寻找任意两个随机输入产生相同哈希值(碰撞)的难度,远低于寻找一个与 特定目标 输入产生碰撞的难度。生日悖论是一个反直觉的概率现象。问题:一个房间里需要有多少人,才能使“至少有两个人生日相同”的概率超过 50%?事实答案:只需要 23 人。在 23 人中,至少两人生日相同的概率就超过了 50%。当人数达到 70 人时,这个概率高达 99.9%。为什么直觉会错?因为我们下意识地在想“任何一个人和我生日相同”的概率。这确实很低(23 人中,和你同生日的概率只有约 6%)。但“生日悖论”问的是“任意两个人之间生日相同”。随着人数增加,人与人之间可能的配对数量呈平方级增长(23 个人,可以形成
(23*22)/2=253对不同的组合)。在这些大量的配对中,找到一对生日相同的可能性就大大增加了。
所以,当你使用 SHA-256 时(比如在比特币、Git 版本控制、文件完整性校验、数字签名中),完全可以相信:如果两个数据的 SHA-256 值相同,那么它们一定是同一个数据。 这是一个在工程和科学上可以依赖的确定性结论。
MAC
MAC (Message Authentication Code,消息认证码) 是密码学中用于验证消息完整性和来源真实性的一种技术。你可以把它简单理解为:带有密码的哈希值(Keyed Hash)。它解决的核心问题是:“我收到的这条消息,不仅没有被篡改过,而且确确实实是那个持有密码的人发给我的。”
Alice 将消息 m 和其哈希值 h 一起发送给 Bob;Bob 验证 H(m) = h,确保了消息完整性。但入侵者也可以假装是 Alice 并且发送 (m', H(m')),那么如何确保信息就是 Alice 发来的呢?
Alice 和 Bob 需要一个共同的密钥 s,并发送 (m, H(m + s)),而这个带有密码的哈希值 H(m + s) 就称为 MAC。
注意,这个过程中并没有涉及明文-密文的转换。MAC 的应用场景只关心消息的完整性和真实性,不关心消息的保密性。
However, to allow the receiver to be able to detect replay attacks, the message itself must contain data that assures that this same message can only be sent once (e.g. time stamp, sequence number or use of a one-time MAC). Otherwise an attacker could – without even understanding its content – record this message and play it back at a later time, producing the same result as the original sender.
MAC 有很多种实现方式,目前工业界的事实标准是 HMAC-SHA256,基于 SHA-256 算法实现的 MAC。
数字签名
Bob 使用他的私钥签名一份文件(通常是签名文件摘要/哈希值),Alice 使用 Bob 的公钥解密,可以证明这�份文件是 Bob 的。
当 Alice 收到了 Bob 的数字签名,她需要使用 Bob 的公钥来验证。但,如何保证她手上的公钥就是 Bob 的?
CA 负责颁发证书,证书中包含了 Bob 的名字和他的公钥,以此证明这份公钥就是 Bob 的。CA 是有公信力的机构,是我们可以相信的。
证书由 CA 的私钥进行数字签名,Alice 使用 CA 的公钥解密,证明这份证书是 CA 颁发的。但,如何保证她手上 CA 的公钥就是 CA 的呢?
代码签名
代码签名是对应用程序可执行文件的数字签名。
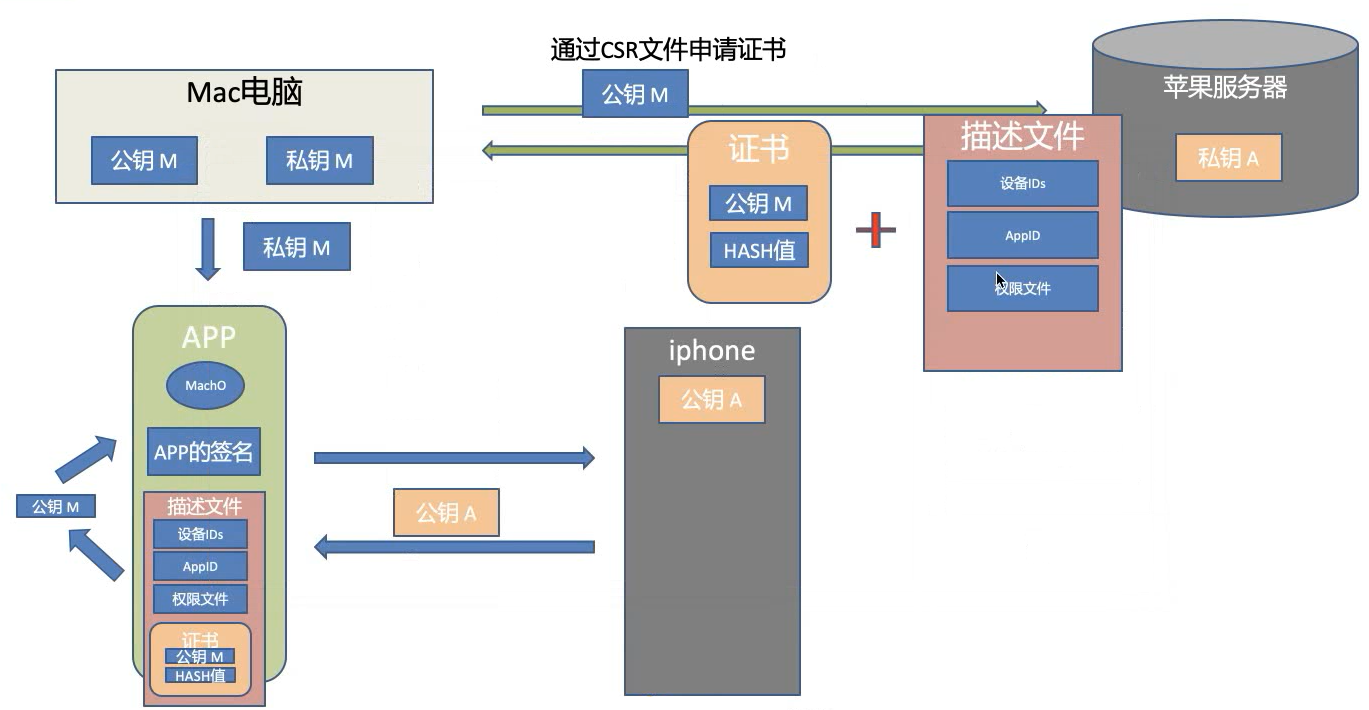
通过 App Store 渠道分发的应用,是怎么签名的:苹果服务器持有私钥,iOS 系统内置公钥。App 上传到 App Store 后,由苹果用私钥签名,下载到手机后,用公钥验证。
iOS 双向签名验证:
- Mac 电脑通过 CSR 文件(本地公钥 M)向 App Store 申请证书和描述文件,由苹果的私钥 A 进行签名。
- Mac 电脑拿到签名后的证书,与本地私钥 M 进行绑定(即导出后的 p12 文件)。
- Xcode 安装时,使用本地私钥 M 对 App 签名,并将可执行文件 + App 签名 + 描述文件 + 证书一起打包。
- iOS 安装时,利用内置的苹果公钥 A 验证证书,证明是苹果颁发的。
- 取出证书中的公钥,验证 App 的签名。
苹果签名三件套:
- Certificate (证书):证明“你是谁”,也就是你的开发者身份
- Entitlements (授权/能力):证明“你的 APP 能干什么”,如使用 iCloud、Push 等
- Provisioning Profile (描述文件):它把上面所有东西捆绑在一起,告诉 iOS 系统“这个证书有权在这个设备上运行这个 App,并使用这些权限”