Runtime
isa
前面学习 NSObject 的时候,我们知道 objc_object 有且仅有一个成员,就是 isa 指针,指向 objc_class 类型。
在 32 位架构时,isa 的确是一个普通的指针,存储着类对象的地址。
但在 64 位架构,isa 进行了优化,使用了 union(共用体)和 bit-field(位域)来存储更多的信息。
union isa_t {
// 数据都存在这里
// printf("%zu\n", sizeof(uintptr_t)); // 8字节,64位
// defines: sys/_types/_uintptr_t.h
uintptr_t bits;
private:
// Accessing the class requires custom ptrauth operations, so
// force clients to go through setClass/getClass by making this
// private.
Class cls;
public:
#if defined(ISA_BITFIELD)
struct {
ISA_BITFIELD; // defined in isa.h
};
#endif
void setClass(Class cls, objc_object *obj);
Class getClass(bool authenticated);
Class getDecodedClass(bool authenticated);
};
可以看到,优化后,同样占用一个指针的内存空间大小,由于使用了位域,bits 中可以存储更多的信息。
#define ISA_MASK 0x0000000ffffffff8ULL
uintptr_t nonpointer : 1; // 0 代表普通的指针类型,存放类对象的内存地址;1 代表优化后、使用位域存储更多信息
uintptr_t has_assoc : 1; // 是否曾经设置过关联对象,如果没有,释放时会更快
uintptr_t has_cxx_dtor : 1; // 是否有 C++ 析构函数(.cxx_destruct),如果没有,释放�时会更快
uintptr_t shiftcls : 33; /*MACH_VM_MAX_ADDRESS 0x1000000000 类对象的内存地址用33位存储就够了 */
uintptr_t magic : 6; // 用于在调试时分辨对象是否完成初始化
uintptr_t weakly_referenced : 1; // 是否曾经被弱引用过,如果没有,释放会更快
uintptr_t unused : 1; // fixme: 是否未被使用过?
uintptr_t has_sidetable_rc : 1; // 当引用计数大小超出 2^19 时,需要另外存在 SideTable 类里
uintptr_t extra_rc : 19 // rc 即 reference count,这里存储的值是引用计数减 1
如果打印类对象地址值会发现,最低 3 位永远是 0,这是由于类对象地址值是存放在低位第 4 位开始。
static void *key = &key;
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
NSLog(@"%p", [NSObject class]); // 0x21de7e330 类对象的地址最后3位永远是0
NSObject *obj = [[NSObject alloc] init];
/**
(lldb) p/x obj->isa
(Class) $0 = 0x010000021de7e331 NSObject
*/
objc_setAssociatedObject(obj, &key, @1, OBJC_ASSOCIATION_ASSIGN); // 此时还未设置关联对象,has_assoc为0
/**
(lldb) p/x obj->isa
(Class) $0 = 0x010000021de7e333 NSObject
*/
objc_removeAssociatedObjects(obj); // has_assoc为1
/**
(lldb) p/x obj->isa
(Class) $0 = 0x010000021de7e333 NSObject
*/
// 就算移除了关联对象,has_assoc仍然为1
return 0;
}
有 cpp 析构、关联对象的对象,释放时会多做一些操作,速度会慢些:
void *objc_destructInstance(id obj)
{
if (obj) {
// Read all of the flags at once for performance.
bool cxx = obj->hasCxxDtor();
bool assoc = obj->hasAssociatedObjects();
// This order is important.
if (cxx) object_cxxDestruct(obj);
if (assoc) _object_remove_assocations(obj, /*deallocating*/true);
obj->clearDeallocating();
}
return obj;
}
method_t
接下来研究类对象里的方法列表。
// 看不到 objc_selector 的源码,但知道它和 char * 类似就可以了
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
// FIXME:
typedef void (*IMP)(void /* id, SEL, ... */ );
struct method_t {
// The representation of a "big" method. This is the traditional
// representation of three pointers storing the selector, types
// and implementation.
struct big {
SEL name; // SEL理解为函数名就可以了
const char *types; // 编码(返回值类型、参数类型)
MethodListIMP imp; // 指向函数的指针(存储着函数的地址)
};
}
不同类中相同名字的方法,所对应的 SEL 是相同的,内存地址都一样。
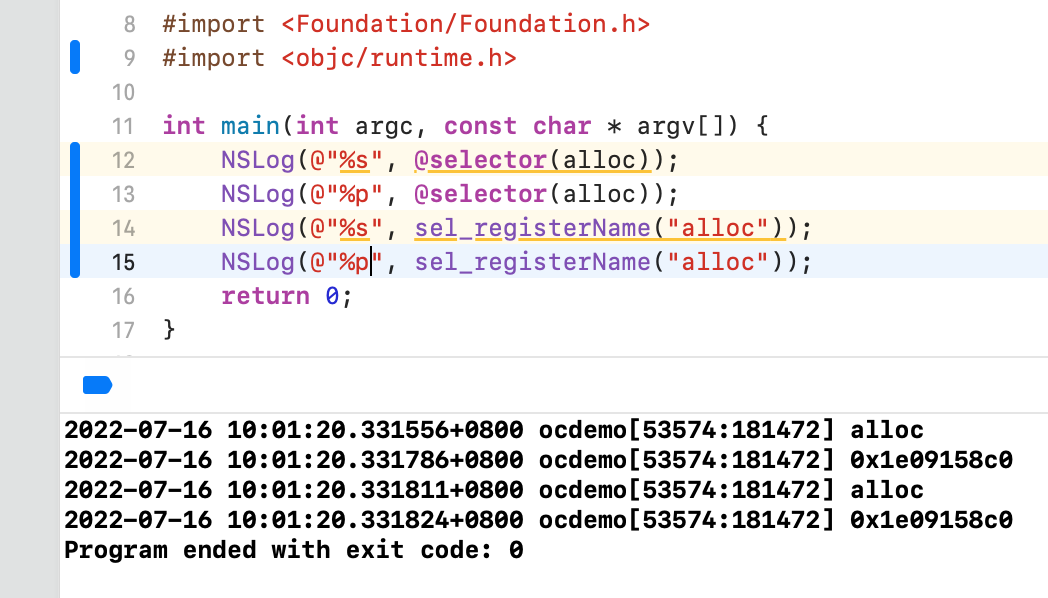
Type Encodings
苹果提供了 @encode 的指令,可以将具体的类型表示为字符串编码,这是为了方便在 Runtime 内部表示类型。
int main(int argc, const char * argv[]) {
NSLog(@"%s", @encode(int)); // i
NSLog(@"%s", @encode(id)); // @
NSLog(@"%s", @encode(SEL)); // :
return 0;
}
具体类型可以查阅:Type Encodings
方法缓存
struct cache_t {
struct bucket_t *buckets() const; // hashtable
mask_t mask() const; // capacity - 1
mask_t occupied() const; // 已经缓存的方法数量
}
struct bucket_t {
explicit_atomic<uintptr_t> _imp; // 函数地址
explicit_atomic<SEL> _sel; // SEL 作为 hashtable 的 key
}
哈希函数常见的实现是模除和位与,苹果用的是位与。方法在 hashtable 中的索引是 sel & mask 计算出来的(数字 A 位与或模除运算的结果,一定小于等于数字 A)。由于最大的索引是 capacity - 1,因此 mask 的值就是 capacity - 1。
static inline mask_t cache_next(mask_t i, mask_t mask) {
return i ? i-1 : mask; // 哈希冲突时采用线性探测,减一,很简单的实现
}
static inline mask_t cache_hash(SEL sel, mask_t mask)
{
uintptr_t value = (uintptr_t)sel;
return (mask_t)(value & mask);
}
void cache_t::insert(SEL sel, IMP imp, id receiver)
{
// 插入前的准备工作:对容量进行检查、必要时扩容
// Use the cache as-is if until we exceed our expected fill ratio.
mask_t newOccupied = occupied() + 1;
unsigned oldCapacity = capacity(), capacity = oldCapacity;
if (slowpath(isConstantEmptyCache())) {
// Cache is read-only. Replace it.
if (!capacity) capacity = INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, /* freeOld */false);
}
else if (fastpath(newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= cache_fill_ratio(capacity))) {
// Cache is less than 3/4 or 7/8 full. Use it as-is.
}
#if CACHE_ALLOW_FULL_UTILIZATION
else if (capacity <= FULL_UTILIZATION_CACHE_SIZE && newOccupied + CACHE_END_MARKER <= capacity) {
// Allow 100% cache utilization for small buckets. Use it as-is.
}
#endif
else {
capacity = capacity ? capacity * 2 : INIT_CACHE_SIZE;
if (capacity > MAX_CACHE_SIZE) {
capacity = MAX_CACHE_SIZE;
}
reallocate(oldCapacity, capacity, true);
}
bucket_t *b = buckets();
mask_t m = capacity - 1;
mask_t begin = cache_hash(sel, m);
mask_t i = begin;
// Scan for the first unused slot and insert there.
// There is guaranteed to be an empty slot.
do {
if (fastpath(b[i].sel() == 0)) {
incrementOccupied();
b[i].set<Atomic, Encoded>(b, sel, imp, cls());
return;
}
if (b[i].sel() == sel) {
// The entry was added to the cache by some other thread
// before we grabbed the cacheUpdateLock.
return;
}
} while (fastpath((i = cache_next(i, m)) != begin));
}
// 扩容时不会将原来的方法缓存复制过来的,扩容后原来的方法缓存就没有了
void cache_t::reallocate(mask_t oldCapacity, mask_t newCapacity, bool freeOld)
{
bucket_t *oldBuckets = buckets();
bucket_t *newBuckets = allocateBuckets(newCapacity);
setBucketsAndMask(newBuckets, newCapacity - 1);
if (freeOld) {
collect_free(oldBuckets, oldCapacity);
}
}
fastpath 和 slowpath
在 objc 源码里定义了两个宏:
#define fastpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1))
#define slowpath(x) (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 0))
long __builtin_expect (long exp, long c) 是 gcc 编译器的内置函数,它的作用是告诉编译器,哪个分支更有可能被执行。编译器会将更有可能执行的分支的机器�码紧密排列在一起,减少指令跳转带来的性能损耗。
例如 (__builtin_expect(bool(x), 1)) 告诉编译器,x == 1 的可能性很大,大部分情况下都会走这个分支,因此命名为 fastpath。
objc_msgSend
方法调用可以分为三个阶段:1. 消息发送;2. 动态方法解析;3. 消息转发。
在学习 NSObject 时,我们将 oc 代码重写为 cpp 代码后发现,oc 的方法调用在底层都是 objc_msgSend 函数,在 objc 源码里它是用汇编实现的。
ENTRY _objc_msgSend
UNWIND _objc_msgSend, NoFrame
// x0寄存器,即objc_msgSend的第一个参数,即消息接收者
cmp p0, #0 // nil check and tagged pointer check
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
// b代表跳转,le即less equal,当x0<=0时,跳转到LNilOrTagged
b.le LNilOrTagged // (MSB tagged pointer looks negative)
#else
// 如果消息接收者为0,直接返回0了
b.eq LReturnZero
#endif
ldr p13, [x0] // p13 = isa
GetClassFromIsa_p16 p13, 1, x0 // p16 = class
LGetIsaDone:
// calls imp or objc_msgSend_uncached
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSend, __objc_msgSend_uncached
#if SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
LNilOrTagged:
b.eq LReturnZero // nil check
GetTaggedClass
b LGetIsaDone
// SUPPORT_TAGGED_POINTERS
#endif
LReturnZero:
// x0 is already zero
mov x1, #0
movi d0, #0
movi d1, #0
movi d2, #0
movi d3, #0
ret
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSend
.macro MethodTableLookup
SAVE_REGS MSGSEND
// lookUpImpOrForward(obj, sel, cls, LOOKUP_INITIALIZE | LOOKUP_RESOLVER)
// receiver and selector already in x0 and x1
mov x2, x16
mov x3, #3
bl _lookUpImpOrForward
// IMP in x0
mov x17, x0
RESTORE_REGS MSGSEND
_lookUpImpOrForward 对应 C/C++ 的代码应该去掉最前面的一个下划线,因此在 objc 源码里找 lookUpImpOrForward 方法。
NEVER_INLINE
IMP lookUpImpOrForward(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
const IMP forward_imp = (IMP)_objc_msgForward_impcache;
IMP imp = nil;
// 第一步,self/superclass 方法列表查找
for (unsigned attempts = unreasonableClassCount();;) {
// curClass method list.
Method meth = getMethodNoSuper_nolock(curClass, sel);
if (meth) {
imp = meth->imp(false); // 找到了
goto done;
}
// getSuperclass一直往父类里找
if (slowpath((curClass = curClass->getSuperclass()) == nil)) {
// No implementation found, and method resolver didn't help.
// Use forwarding.
imp = forward_imp; // 1、2步都没找到,最后第3步拿forward_imp兜底
break;
}
}
// 第二步
// No implementation found. Try method resolver once.
if (slowpath(behavior & LOOKUP_RESOLVER)) {
behavior ^= LOOKUP_RESOLVER;
return resolveMethod_locked(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
}
static NEVER_INLINE IMP
resolveMethod_locked(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls, int behavior)
{
if (! cls->isMetaClass()) {
// try [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
else {
// try [nonMetaClass resolveClassMethod:sel]
// and [cls resolveInstanceMethod:sel]
resolveClassMethod(inst, sel, cls);
if (!lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls)) {
resolveInstanceMethod(inst, sel, cls);
}
}
// 调用解析器可能已经填充了缓存
// chances are that calling the resolver have populated the cache
// so attempt using it
return lookUpImpOrForwardTryCache(inst, sel, cls, behavior);
}
static void resolveInstanceMethod(id inst, SEL sel, Class cls)
{
SEL resolve_sel = @selector(resolveInstanceMethod:);
BOOL (*msg)(Class, SEL, SEL) = (typeof(msg))objc_msgSend; // 向类发送resolveInstanceMethod:消息
bool resolved = msg(cls, resolve_sel, sel);
// 把动态解析的方法缓存下来了,下次就不用动态解析了
// Cache the result (good or bad) so the resolver doesn't fire next time.
// +resolveInstanceMethod adds to self a.k.a. cls
IMP imp = lookUpImpOrNilTryCache(inst, sel, cls);
}
_objc_msgForward_impcache 的实现可以在汇编代码里找到:
STATIC_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
// No stret specialization.
b __objc_msgForward
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward_impcache
ENTRY __objc_msgForward
adrp x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGE
ldr p17, [x17, __objc_forward_handler@PAGEOFF]
TailCallFunctionPointer x17
END_ENTRY __objc_msgForward
查到 objc_defaultForwardHandler 这里,就找不到了,因为接下来的代码没有开源。但已有国外大神通过逆向整理出 ___forwarding___ 的伪代码,因实战意义不大,这里不继续探究了。
objc_msgSendSuper
我们重写一段常见的代码为 cpp,来探究 super 关键字背后的原理:
@interface Demo : NSObject
- (void)test;
@end
@implementation Demo
- (void)test {
Class superCls = [super class];
NSLog(@"%@", superCls); // 为什么是Demo?
}
@end
static void _I_Demo_test(Demo * self, SEL _cmd) {
Class superCls = objc_msgSendSuper((__rw_objc_super){
(id)self, // receiver
(id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Demo"))
}, sel_registerName("class"));
NSLog((NSString *)&__NSConstantStringImpl__var_folders_yb_d6gg31rn7snd9rnp12sctfb00000gn_T_Demo_52f45a_mi_0, superCls);
}
struct objc_super {
/// Specifies an instance of a class.
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull id receiver;
/// Specifies the particular superclass of the instance to message.
__unsafe_unretained _Nonnull Class super_class;
/* super_class is the first class to search */
};
/**
* @param super A pointer to an \c objc_super data structure. Pass values identifying the
* context the message was sent to, including the instance of the class that is to receive the
* message and the superclass at which to start searching for the method implementation.
*/
OBJC_EXPORT id _Nullable
objc_msgSendSuper(struct objc_super * _Nonnull super, SEL _Nonnull op, ...);
可以看到,虽然我们调用 [super class],但消息接收者仍然是 self 对象!而且是指从父类开始查找方法的实现!
由于 class 的实现是在 NSObject,因此无论是 [self class] 或是 [super class],最后都是跳转到 NSObject 的 IMP,而消息接收者是 self 对象,因此打印出来的类名仍然是当前类的类名,而不是父类的类名。
super 引出的函数调用分析
看下面这个例子:
@interface Demo : NSObject
@property (nonatomic, copy) NSString *name;
- (void)print;
@end
@implementation Demo
- (void)print {
NSLog(@"%@", self.name); // ptr->cls, cls 偏移8个字节的位置,就是栈上的 hello 变量!
}
@end
@interface ViewController : UIViewController
@end
@implementation ViewController
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
// 栈空间由高地址向低地址伸展
long long a = 1;
long long b = 2;
NSString *hello = @"hello";
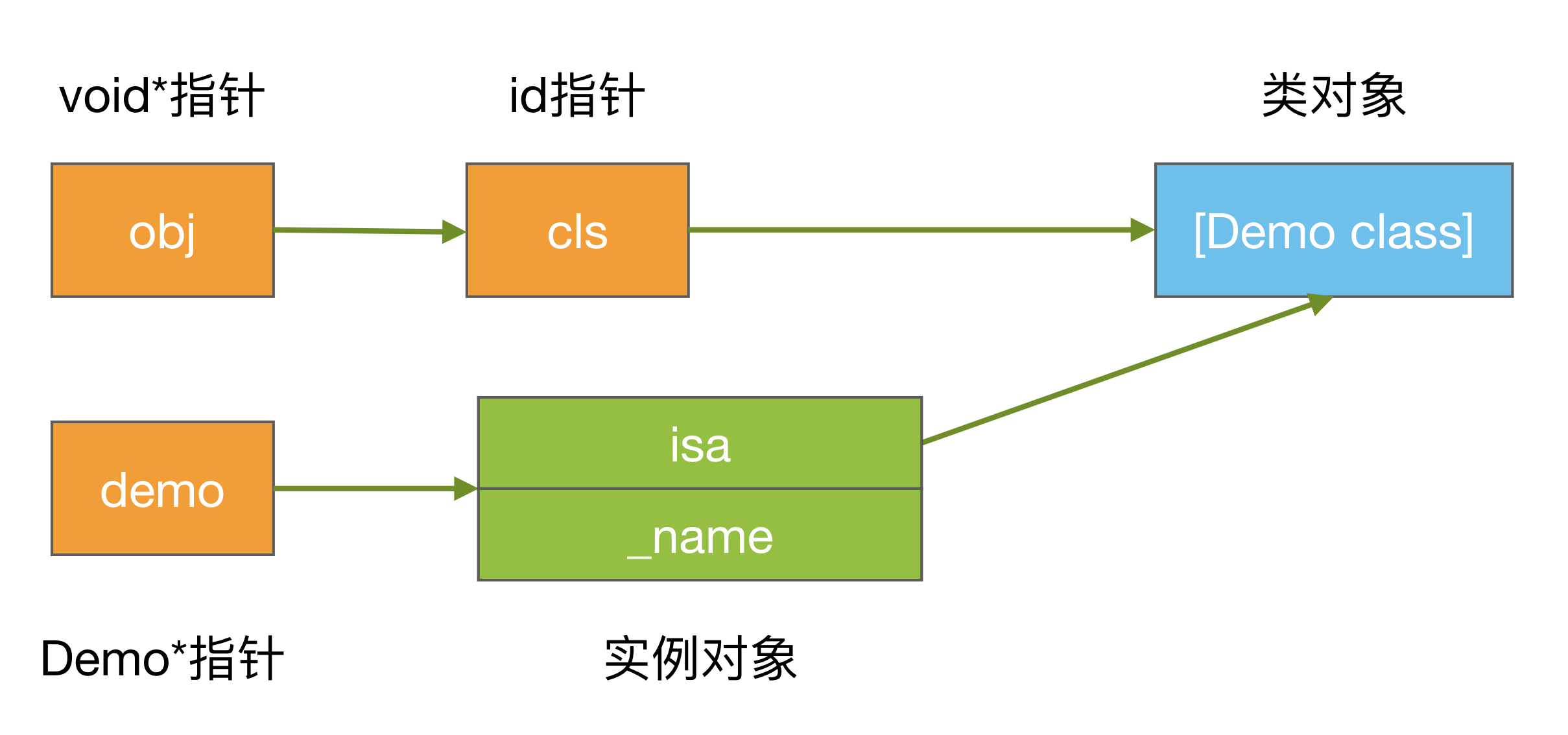
id cls = [Demo class]; // typedef struct objc_object *id;
void *ptr = &cls;
[(__bridge id)ptr print]; // 打印出来是"hello",为什么?
// objc_msgSend(ptr, "print");
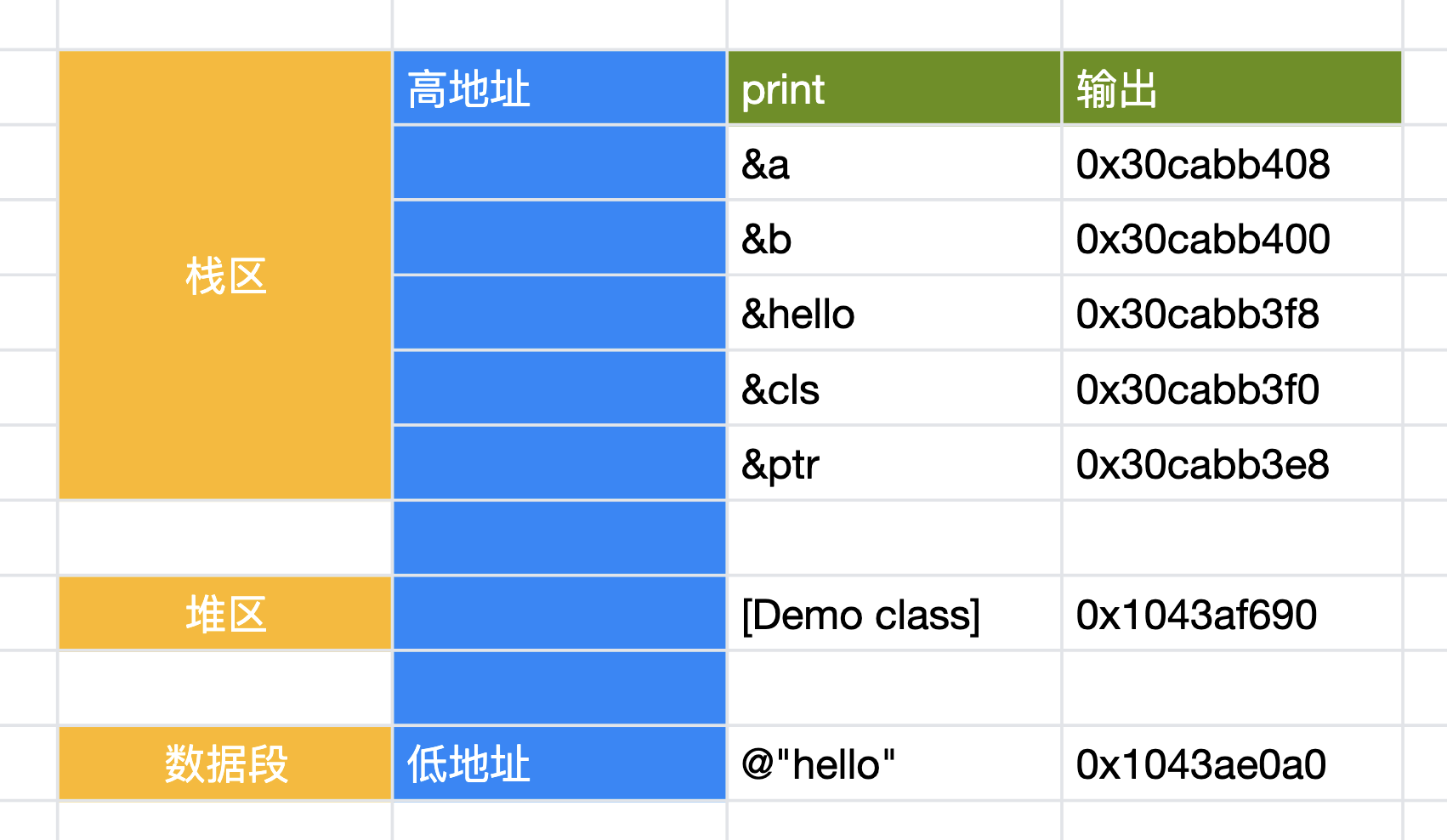
NSLog(@"%p, %p", &a, &b);
NSLog(@"%p, %p", &hello, hello);
NSLog(@"%p, %p", &cls, cls);
NSLog(@"%p", &ptr);
}
@end
内存结构:
如果将上述代码修改成:
- (void)viewDidLoad {
[super viewDidLoad];
id cls = [Demo class];
void *ptr = &cls;
[(__bridge id)ptr print];
}
打印出来将是 ViewController 的实例对象,为什么?原因是 [super viewDidLoad] 调用在底层创建了临时结构体:
(__rw_objc_super){
(id)self, // 低地址
(id)class_getSuperclass(objc_getClass("Demo")) // 高地址
}
cls 指针顺着偏移 8 个字节,将是 self 对象。
汇编代码与中间代码
注意,刚才我们是通过重写为 cpp 代码的方式来探索底层,真正运行时的调用跟 cpp 代码有区别,如果断点在汇编代码,会看到调用的其实是 objc_msgSendSuper2,找到这个函数的汇编实现:
ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2
UNWIND _objc_msgSendSuper2, NoFrame
#if __has_feature(ptrauth_calls)
ldp x0, x17, [x0] // x0 = real receiver, x17 = class
add x17, x17, #SUPERCLASS // x17 = &class->superclass
ldr x16, [x17] // x16 = class->superclass
AuthISASuper x16, x17, ISA_SIGNING_DISCRIMINATOR_CLASS_SUPERCLASS
LMsgSendSuperResume:
#else
ldp p0, p16, [x0] // p0 = real receiver, p16 = class
ldr p16, [x16, #SUPERCLASS] // p16 = class->superclass
#endif
L_objc_msgSendSuper2_body:
CacheLookup NORMAL, _objc_msgSendSuper2, __objc_msgSend_uncached
END_ENTRY _objc_msgSendSuper2
发现 objc_msgSendSuper2 调用时,x0 是消息接收者也就是 self,但 x17 是 class 本身而不是 superclass,这个跟 cpp 代码是有区别的(但这些微小差别不影响我们用重写为 cpp 代码的方式来探究底层原理)。
通过将实现文件转为汇编代码,并搜索实现文件中的行号,也可以找到底层的实现:
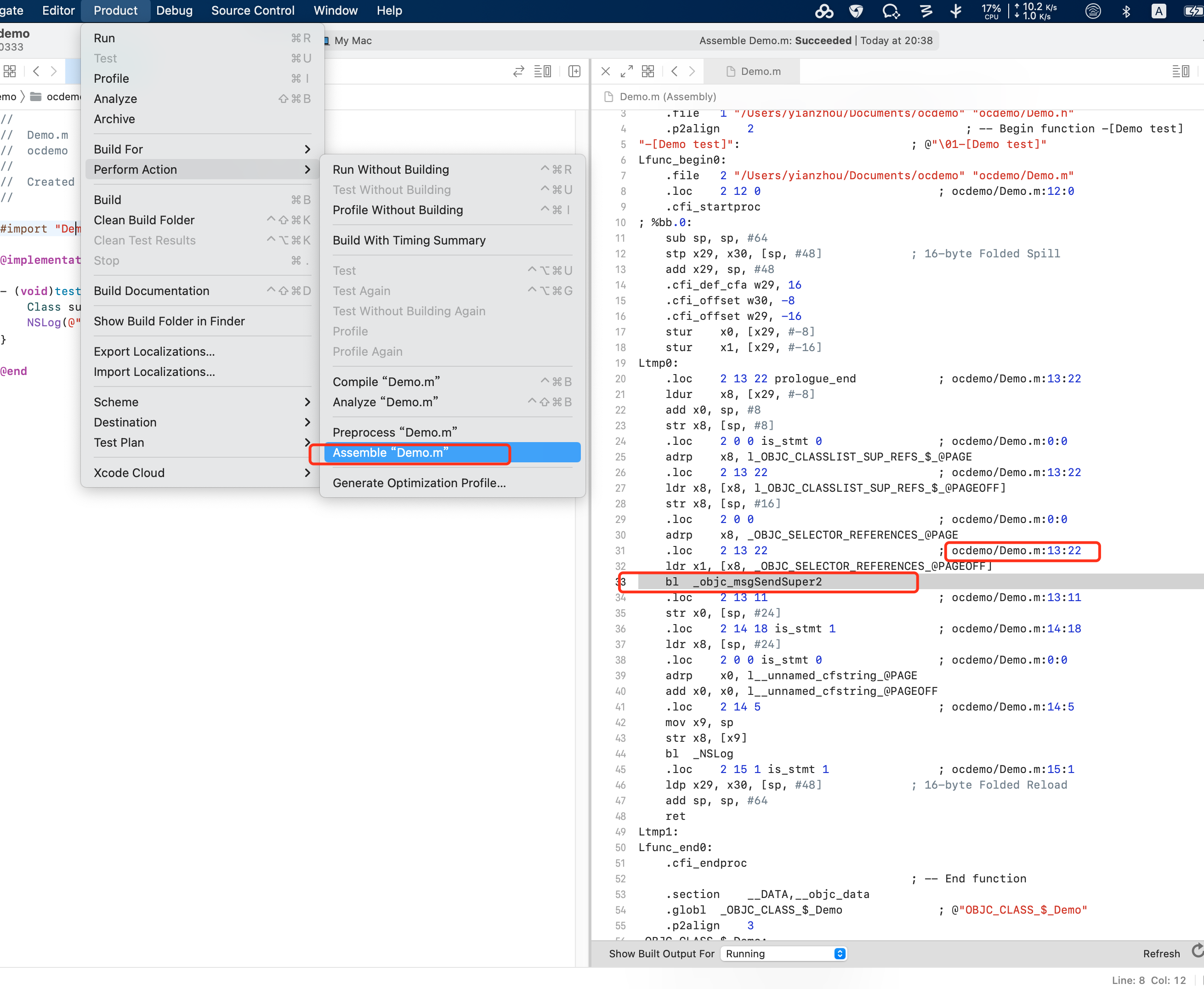
还有一种方法可以窥探底层实现。苹果在真正编译我们的程序时,在 objc 和汇编代码的中间,并不是 cpp,而是一种中间代码,后缀为 ll(代表 LLVM),其语法可参考 https://llvm.org/docs/LangRef.html
中间代码是平台无关的。编译时,高级语言的代码先转成中间代码,再转成具体架构的汇编代码,最后转成机器码。
用以下指令转成的 Demo.ll 文件中,同样能找到 objc_msgSendSuper2 的调用:
clang -emit-llvm -S Demo.m
方法交换
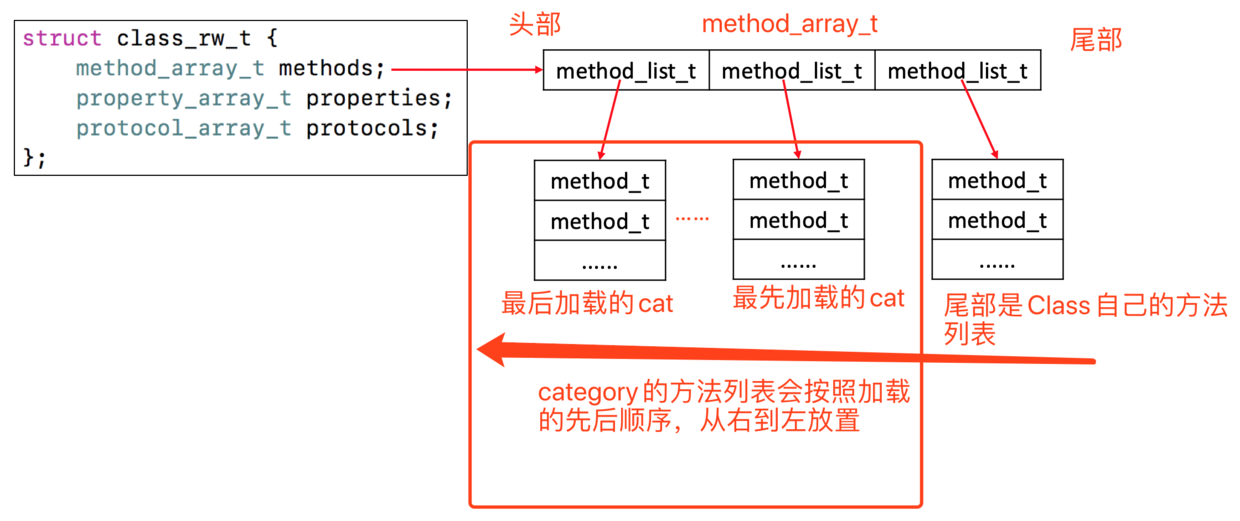
方法交换,交换的是 struct class_rw_t 里的 method_array_t methods 里的 struct method_t 里的 MethodListIMP imp,它存储着函数的地址,所以交换的是函数实现的地址。
调用 method_exchangeImplementations 方法时,会清空方法缓存。
void method_exchangeImplementations(Method m1, Method m2)
{
if (!m1 || !m2) return;
mutex_locker_t lock(runtimeLock);
IMP imp1 = m1->imp(false);
IMP imp2 = m2->imp(false);
SEL sel1 = m1->name();
SEL sel2 = m2->name();
m1->setImp(imp2);
m2->setImp(imp1);
// 清空方法缓存
flushCaches(nil, __func__, [sel1, sel2, imp1, imp2](Class c){
return c->cache.shouldFlush(sel1, imp1) || c->cache.shouldFlush(sel2, imp2);
});
adjustCustomFlagsForMethodChange(nil, m1);
adjustCustomFlagsForMethodChange(nil, m2);
}
数组越界如何保护
访问数组内元素有两种接口,一种是下标访问 arr[1],实际上是调用了 objectAtIndexedSubscript:;一种是 NSArray 的实例方法 objectAtIndex:。
NSArray *array = @[@0, @1];
array[2]; // crash
[array objectAtIndex:2]; // crash
可以为 NSArray 创建一个分类:NSArray+Safe.h,添加安全的索引方法,但获取类对象时要注意,NSArray 是一个类簇,其背后有各种具体实现的子类!
#import <objc/runtime.h>
+ (void)load {
// 注意!NSArray 背后是一个类簇
swizzleInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndex:), @selector(safeObjectAtIndex:));
swizzleInstanceMethod(objc_getClass("__NSArrayI"), @selector(objectAtIndexedSubscript:), @selector(safeObjectAtIndexedSubscript:));
}
- (id)safeObjectAtIndex:(NSUInteger)index {
if (index >= self.count || index < 0) {
return nil;
} else {
return [self safeObjectAtIndex:index];
}
}
- (id)safeObjectAtIndexedSubscript:(NSUInteger)index {
if (index >= self.count || index < 0) {
return nil;
} else {
return [self safeObjectAtIndexedSubscript:index];
}
}
参考实现:NSObject-Safe
消息发送
方法的调用实际上是消息发送:objc_msgSend(demo, @selector(test), params);。
通过 isa 指针找到类对象,里面有 struct objc_method_list 和 struct objc_cache。
根据 selector 的名字,在类对象的缓存列表中查找(本质是字符串匹配),如果没有命中,则在方法列表中查找,找到后缓存下来,并跳转到方法的实现;下次发送同一消息时,命中缓存列表,直接跳转到方法的实现。
如果在方法列表里没有找到,通过 super_class 指针往父类里查找,一直到 NSObject 都没有找到的话,则用 objc_msgForward 函数指针代替 IMP,最后,执行这个 IMP(启动消息转发机制,即动态方法决议、替补接收者、完整消息转发三步走)。
纯 Swift 类,在编译期即通过 V-Table 确定了函数的调用,直接从虚函数表通过索引取出函数的内存地址来调用,不具备运行时消息转发机制。
在 OC 中,对方法的调用都会被转换成 objc_msgSend 方法的调用。示例如下:
// 1、创建对象
// 给 MessageSendTest 类发送消息,创建对象
// 等同于:MessageSendTest *test = [MessageSendTest alloc];
MessageSendTest *test = ((MessageSendTest * (*)(id,SEL)) objc_msgSend)((id) [MessageSendTest class], @selector(alloc));
// 2、初始化对象
// 给 test 对象发送消息进行初始化
// 等同于:[test init];
test = ((MessageSendTest *(*)(id,SEL))objc_msgSend)((id) test, @selector(init));
// 3、调用无参无返回值方法
// 等同于
((void(*)(id, SEL))objc_msgSend)((id) test, @selector(noArgumentsAndNoReturnValue));
// 4、调用带一个参数但无返回值的方法
((void(*)(id, SEL, NSString *))objc_msgSend)((id) test, @selector(hasArguments:), @"参数");
// 5、调用带参数带返回值的方法。
int result = ((int *(id, SEL, NSString *, int))objc_msgSend)((id) test, @selector(hasArguments:andReturnValue:), @"参数", 1024);
Selector、Method、IMP 的关系:在 Runtime 中,类对象和 MetaClass 都有方法列表,方法列表中的每一个元素就是一个 Method,它的名称就是 Selector,对应着一个方法实现(IMP)。方法交换就是将 SEL 和 IMP 原本的对应断开,并生成新的对应关系。
/// An opaque type that represents a method selector.
typedef struct objc_selector *SEL;
/// A pointer to the function of a method implementation.
#if !OBJC_OLD_DISPATCH_PROTOTYPES
typedef void (*IMP)(void /* id, SEL, ... */ );
#else
typedef id (*IMP)(id, SEL, ...);
#endif
/// An opaque type that represents a method in a class definition.
typedef struct objc_method *Method;
struct objc_method {
SEL method_name;
char *method_types;
IMP method_imp;
}
Weak 的实现探索
初始化一个 weak 指针,可以分为两种情况:
// (The nil case)
__weak id weakPtr;
// (The non-nil case)
NSObject *o = ...;
__weak id weakPtr = o;
我们通过查看汇编发现初始化 weak 指针底层调用的是 objc_initWeak,打开 Runtime 源码,找到这个方法:
/*
* @param location Address of __weak ptr.
* @param newObj Object ptr.
*/
id objc_initWeak(id *location, id newObj)
{
if (!newObj) {
*location = nil;
return nil;
}
return storeWeak<false/*old*/, true/*new*/, true/*crash*/>
(location, (objc_object*)newObj);
}
template <bool HaveOld, bool HaveNew, bool CrashIfDeallocating>
static id storeWeak(id *location, objc_object *newObj)
{
// ..
SideTable *oldTable; // 旧对象所在的 SideTable
SideTable *newTable; // 新对象所在的 SideTable
retry:
if (HaveOld) {
oldObj = *location;
// SideTables 是一个全局的 StripedMap,是一个固定容量为 64 的数组。
oldTable = &SideTables()[oldObj];
} else {
oldTable = nil;
}
if (HaveNew) {
// SideTables 是一个全局的 StripedMap,是一个固定容量为 64 的数组。
newTable = &SideTables()[newObj];
} else {
newTable = nil;
}
if (HaveNew) {
/**
* Registers a new (object, weak pointer) pair. Creates a new weak
* object entry if it does not exist.
*
* @param weak_table The global weak table.
* @param referent The object pointed to by the weak reference.
* @param referrer The weak pointer address.
*/
newObj = (objc_object *)weak_register_no_lock(&newTable->weak_table,
(id)newObj, location,
CrashIfDeallocating);
// Set is-weakly-referenced bit in refcount table.
if (newObj && !newObj->isTaggedPointer()) {
newObj->setWeaklyReferenced_nolock();
}
// weak 指针指向弱引用的对象
*location = (id)newObj;
}
else {
// No new value. The storage is not changed.
}
return (id)newObj;
}
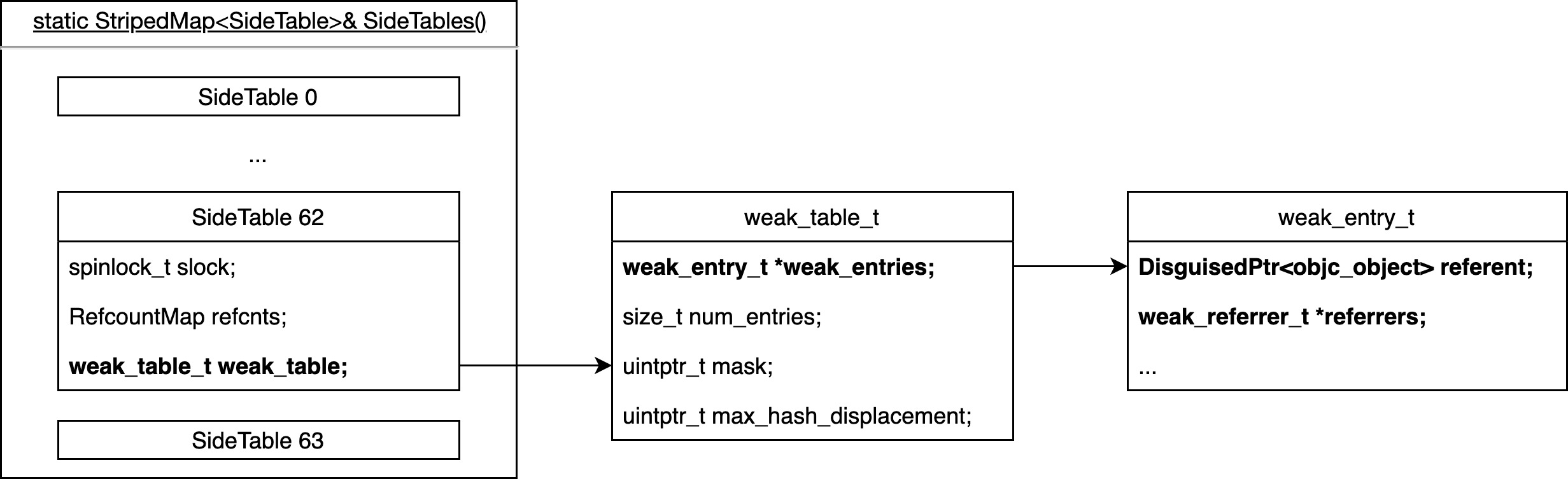
SideTable 用于管理对象的引用计数和弱引用,是一个固定容量为 64 的数组。
static StripedMap<SideTable>& SideTables() {
return *reinterpret_cast<StripedMap<SideTable>*>(SideTableBuf);
}
传入一个对象,根据其内存地址对应到具体的一个 SideTable 上。
struct SideTable {
spinlock_t slock; // 自旋锁,用于保护 SideTable 的并发访问
RefcountMap refcnts; // 引用计数表
weak_table_t weak_table; // 弱引用表
// ...
};
/**
* The global weak references table. Stores object ids as keys,
* and weak_entry_t structs as their values.
*/
struct weak_table_t {
weak_entry_t *weak_entries;
size_t num_entries;
uintptr_t mask;
uintptr_t max_hash_displacement;
};
/**
* The internal structure stored in the weak references table.
* It maintains and stores
* a hash set of weak references pointing to an object.
* If out_of_line==0, the set is instead a small inline array.
*/
#define WEAK_INLINE_COUNT 4
struct weak_entry_t {
// The object pointed to by the weak reference.
DisguisedPtr<objc_object> referent;
union {
struct {
/// The address of a __weak object reference
/// typedef objc_object ** weak_referrer_t;
weak_referrer_t *referrers;
uintptr_t out_of_line : 1;
uintptr_t num_refs : PTR_MINUS_1;
uintptr_t mask;
uintptr_t max_hash_displacement;
};
struct {
// out_of_line=0 is LSB(Least Significant Bit) of one of these (don't care which)
weak_referrer_t inline_referrers[WEAK_INLINE_COUNT];
};
};
};
读到这里,我们终于发现,Runtime 维护的 SideTable 存放着全局的引用计数表和弱引用表,�弱引用表也是一个哈希表的结构,它根据所指对象的地址,映射到一个数组,数组里存放的是 weak 指针的地址。
往全局 weak 引用表里插入新的 weak_entry_t 的操作:
static void weak_entry_insert(weak_table_t *weak_table, weak_entry_t *new_entry)
{
weak_entry_t *weak_entries = weak_table->weak_entries;
assert(weak_entries != nil);
size_t index = hash_pointer(new_entry->referent) & (weak_table->mask);
size_t hash_displacement = 0;
while (weak_entries[index].referent != nil) {
index = (index+1) & weak_table->mask;
hash_displacement++;
}
weak_entries[index] = *new_entry;
weak_table->num_entries++;
if (hash_displacement > weak_table->max_hash_displacement) {
weak_table->max_hash_displacement = hash_displacement;
}
}
当对象不再被强引用、需要销毁时,通过 weak 引用表找到所有的弱引用指针,置为空。
class_rw_ext_t
Class object has a pointer to more data where additional information is stored, called the class_ro_t.
Swift classes and Objective-C classes share this infrastructure, so each Swift class has these data structures as well.
Clean memory is memory that isn’t changed once it’s loaded. The class_ro_t is clean because it’s read-only. Dirty memory is memory that’s changed while the process is running. The class structure is dirtied once the class gets used because the runtime writes new data into it. For example, it creates a fresh method cache and points to it from the class.
When a class first gets used, the runtime allocates additional storage for it, the class_rw_t, for read/write data. In this data structure, we store new information only generated at runtime.
Dirty memory is much more expensive than clean memory, and, is the reason why class data is split into two pieces. The more data that can be kept clean, the better. By separating out data that never changes, that allows for most of the class data to be kept as clean memory.
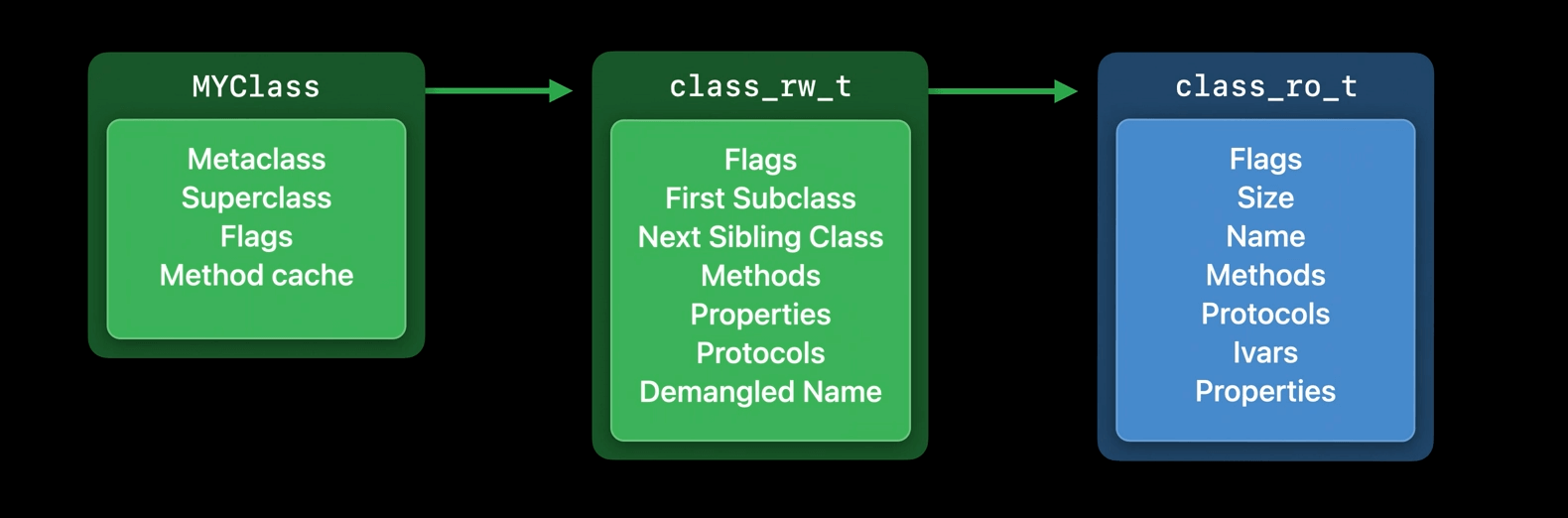
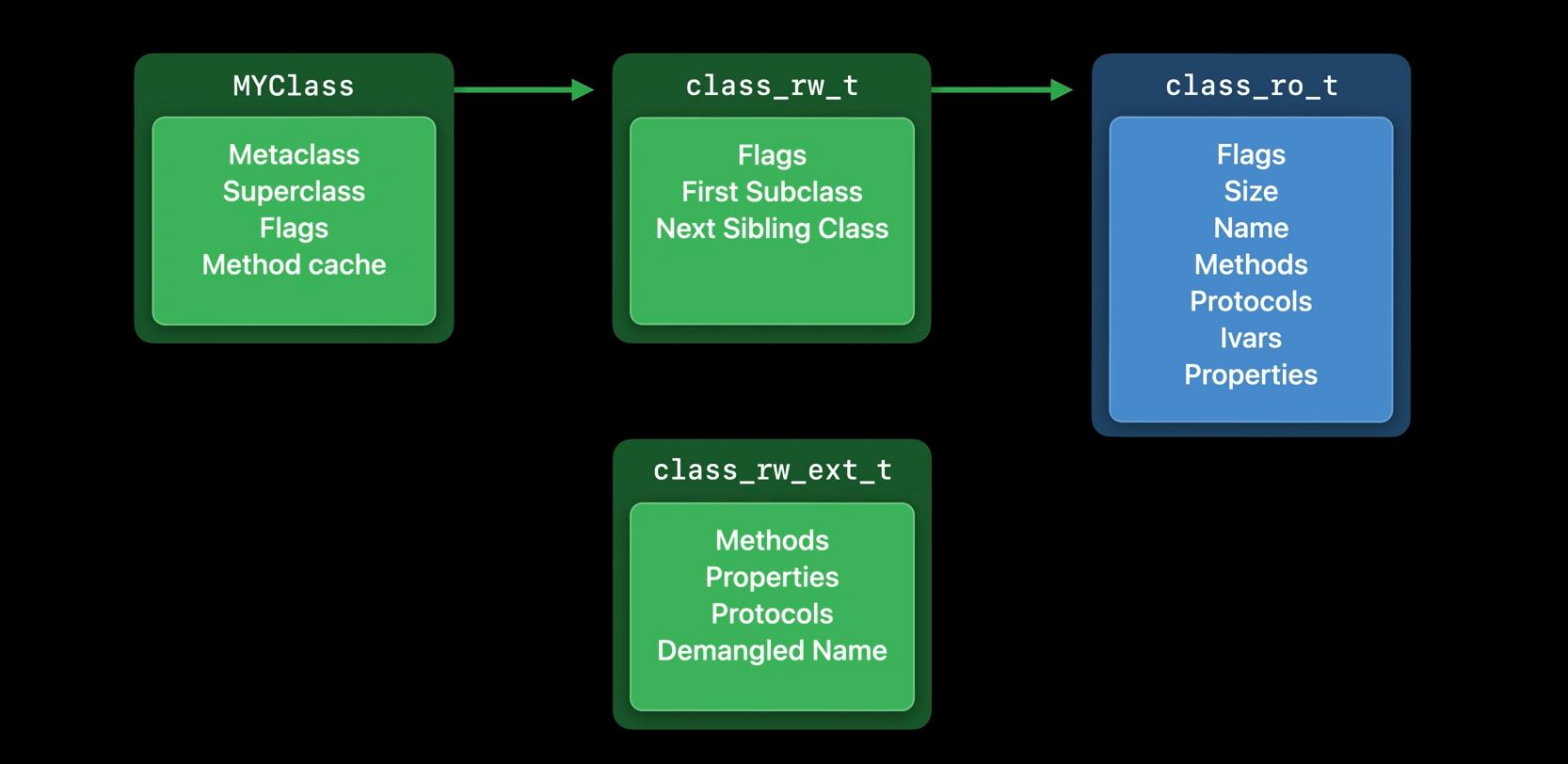
Why do we have methods and properties here when they're in the read-only data too? Because they can be changed at runtime. When a category is loaded, it can add new methods to the class, and the programmer can add them dynamically using runtime APIs. Since the class_ro_t is read-only, we need to track these things in the class_rw_t.
There are a lot of classes in use in any given device. We measured about 30 megabytes of these class_rw_t structures across the system on an iPhone. Examining usage on real devices, we found that only around 10% of classes ever actually have their methods changed at runtime. So, we can split off the parts that aren't usually used to class_rw_ext_t, and this cuts the size of the class_rw_t in half. That saves around 14 megabytes system wide.
To see the impact of this change, you can run heap commands in the terminal. It lets you inspect the heap memory in use by a running process.
> heap Mail | egrep 'class_rw|COUNT'
COUNT BYTES AVG CLASS_NAME TYPE BINARY
6882 220224 32.0 Class.data (class_rw_t) C libobjc.A.dylib
643 30864 48.0 Class.data.extended (class_rw_ext_t) C libobjc.A.dylib
We can see that we're using 6882 of these class_rw_t types in the Mail app, but only about a tenth of them actually needed this extended information.
Method List
Every class has a list of methods attached to it. The runtime uses these lists to resolve message sends. Each method contains three pieces of information:
- First is the method's name or selector. Selectors are strings, but they're unique so they can be compared using pointer equality.
- Next is the method's type encoding. This is a string that represents the parameter and return types, and it isn't used for sending messages, but it's needed for things like runtime introspection and message forwarding.
- Finally, there's a pointer to the method's implementation. When you write a method, it gets compiled into a C function with your implementation in it, and then the entry in the method list points to that function.
Each piece of data in the method list is a pointer. On our 64-bit systems, that means that each method table entry occupies 24 bytes. Now note that a class method entry from a binary only ever points to method implementations within that binary. There's no way to make a method that has its metadata in one binary and the code implementing it in another. That means that method list entries don't actually need to be able to refer to the entire 64-bit address space. So, instead of an absolute 64-bit address, they can use a 32-bit (that is 4 bytes) relative offset within the binary. And that's a change that we've made this year (2020).
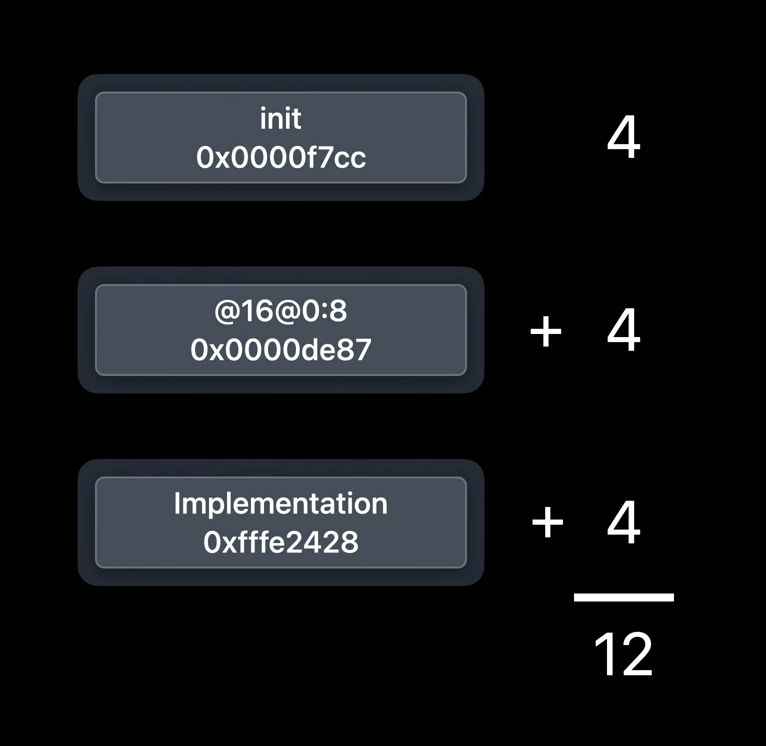
Now, because the offsets are always the same no matter where the image is loaded into memory, they don't have to be fixed up after they're loaded from disk. And, of course, 32-bit offsets mean that we've halved the amount of memory needed on 64-bit platforms. We've measured about 80MB of these methods system wide on a typical iPhone. Since they're half the size, we save 40 megabytes.
But what about swizzling? The method lists in a binary can't now refer to the full address space, but if you swizzle a method, that can be implemented anywhere. To handle this, we also have a global table mapping methods to their swizzled implementations. Swizzling is rare. The vast majority of methods never actually get swizzled, so this table doesn't end up getting very big. Even better, the table is compact. Memory is dirtied a page at a time. With the old style of method lists, swizzling a method would dirty the entire page it was on, resulting in many kilobytes of dirty memory for a single swizzle. With the table, we just pay the cost for an extra table entry.
Tagged Pointer
A normal object pointer have 64 bits, however, we don't really use all of these bits. The low bits are always zero because of alignment requirements. Objects must always be located at an address that's a multiple of the pointer size. The high bits are always zero because the address space is limited. We don't actually go all the way up to 2^64. These high and low bits are always zero.
So, let's pick one of these bits that's always zero and make it a one. That can immediately tell us that this is not a real object pointer, and then we can assign some other meaning to all of the other bits. We call this a tagged pointer.
And another 3 bits indicates the type of the tagged pointer. For example, NSNumber, NSDate. There's a special case for tag seven which indicates an extended tag. An extended tag uses another eight bits to encode the type, allowing for 256 more tag types at the cost of a smaller payload. This allows us to use tagged pointers for more types like UIColor, NSIndexSet.

在 2013 年的 WWDC,Apple 推出了首个 64 位架构的双核处理器,为了节省内存和提高执行效率,苹果引入了 Tagged Pointer。它专门用来存储占用内存很小的对象,例如 NSNumber。Tagged Pointer 不指向任何一个地址,在内存读写上有更高的效率;它并不存储在堆中,也不需要 malloc 和 free,节省了内存空间。
#import <malloc/malloc.h>
#import <objc/runtime.h>
NSNumber *num = [NSNumber numberWithInt:100];
NSLog(@"%zd", malloc_size((__bridge const void *)num)); // 0
NSLog(@"%zd", class_getInstanceSize([NSNumber class])); // 8