RunLoop
介绍
A run loop is an event processing loop that you use to schedule work and coordinate the receipt of incoming events. The purpose of a run loop is to keep your thread busy when there is work to do and put your thread to sleep when there is none.
如果没有 RunLoop,main函数执行完就退出了,App 就无法运行了。
RunLoop 的基本作用:
- 保持程序持续运行不退出
- 处理程序运行中的各种事件(触摸、手势、定时器、网络请求等)
- 没有事件要处理时,休眠,节省 CPU 资源
iOS 中有 2 套 API 可以访问 RunLoop:
- Foundation:
NSRunLoop(ObjC) - Core Foundation:
CFRunLoopRef(C)
CFRunLoopRef 是开源的:https://opensource.apple.com/tarballs/CF/,NSRunLoop 是基于 CFRunLoopRef 的封装。
RunLoop 的基本知识:
- 每个线程都有唯一的与之对应的 RunLoop 对象,保存在全局的字典里
- 线程刚创建时没有 RunLoop 对象,RunLoop 会在第一次获取它时创建,在线程结束时销毁
Your application does not need to create these objects explicitly; each thread, including the application’s main thread, has an associated run loop object. Only secondary threads need to run their run loop explicitly, however. The app frameworks automatically set up and run the run loop on the main thread as part of the application startup process.
CFRunLoopRef CFRunLoopGetCurrent(void) {
CHECK_FOR_FORK();
CFRunLoopRef rl = (CFRunLoopRef)_CFGetTSD(__CFTSDKeyRunLoop);
if (rl) return rl;
return _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_self());
}
static CFMutableDictionaryRef __CFRunLoops = NULL;
static CFLock_t loopsLock = CFLockInit;
CF_EXPORT CFRunLoopRef _CFRunLoopGet0(pthread_t t) {
if (pthread_equal(t, kNilPthreadT)) {
t = pthread_main_thread_np(); // t为空的话就默认主线程
}
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
if (!__CFRunLoops) { // 全局字典不存在,创建
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
CFMutableDictionaryRef dict = CFDictionaryCreateMutable(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, 0, NULL, &kCFTypeDictionaryValueCallBacks);
CFRunLoopRef mainLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(pthread_main_thread_np()); // 默认给主线程创建RunLoop,并加到字典里
CFDictionarySetValue(dict, pthreadPointer(pthread_main_thread_np()), mainLoop);
if (!OSAtomicCompareAndSwapPtrBarrier(NULL, dict, (void * volatile *)&__CFRunLoops)) {
CFRelease(dict);
}
CFRelease(mainLoop);
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
}
CFRunLoopRef loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
if (!loop) {
CFRunLoopRef newLoop = __CFRunLoopCreate(t); // 当前线程没有RunLoop则创建,并加到字典里
__CFLock(&loopsLock);
loop = (CFRunLoopRef)CFDictionaryGetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t));
if (!loop) {
CFDictionarySetValue(__CFRunLoops, pthreadPointer(t), newLoop);
loop = newLoop;
}
// don't release run loops inside the loopsLock, because CFRunLoopDeallocate may end up taking it
__CFUnlock(&loopsLock);
CFRelease(newLoop);
}
return loop;
}
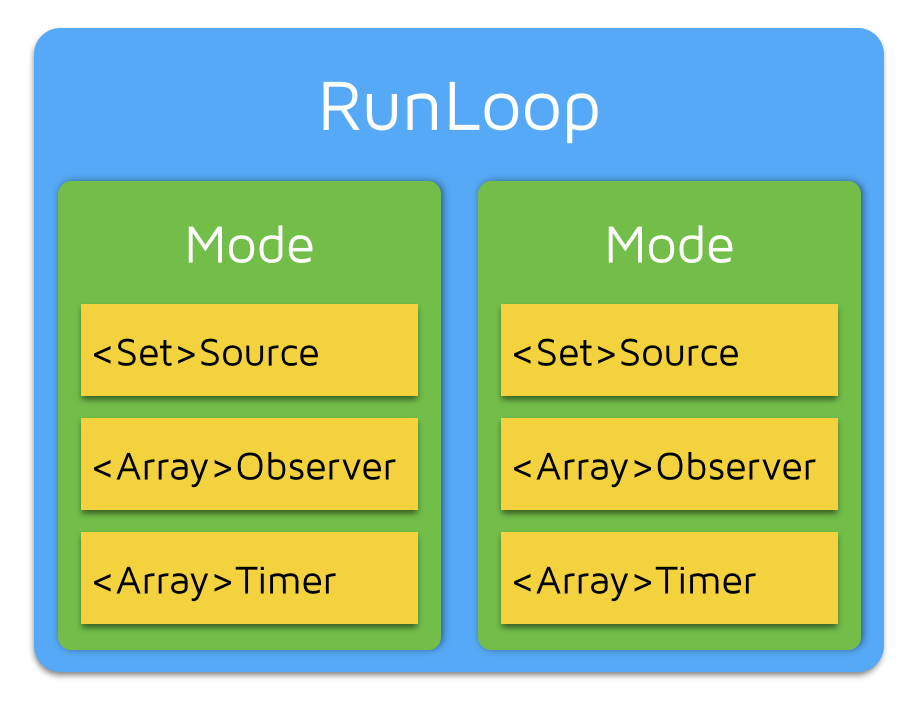
Mode
struct __CFRunLoop {
pthread_t _pthread; // 对应的线程
CFMutableSetRef _commonModes; // 标记哪些模式是 common 模式
CFMutableSetRef _commonModeItems; // 加到 commonMode 的 Source/Observer/Timer 放在这
CFRunLoopModeRef _currentMode; // 当前运行的模式
CFMutableSetRef _modes; // 装着 CFRunLoopModeRef,这些是实际运行的模式
};
struct __CFRunLoopMode {
CFStringRef _name; // 模式的名称
CFMutableSetRef _sources0; // 装着 CFRunLoopSourceRef
CFMutableSetRef _sources1; // 装着 CFRunLoopSourceRef
CFMutableArrayRef _observers; // 装着 CFRunLoopObserverRef
CFMutableArrayRef _timers; // 装着 CFRunLoopTimerRef
};
__CFRunLoopMode 代表 RunLoop 运行的模式,同一时间 RunLoop 只能以一种模式运行。如果要切换模式,则需要退出当前的 RunLoop,并选择新的模式重新进入。这样做可以隔离开不同模式的 Source/Timer/Observer,使其互不影响。
Source/Timer/Observer 这些可以理解为 RunLoop 要处理的事情。RunLoop 以 UITrackingRunLoopMode 运�行时要处理的事情,肯定比以 kCFRunLoopDefaultMode 运行时少得多,苹果这样做可以保持滑动时候的流畅性。
如果 RunLoop 里面没有任何的 Source/Timer/Observer,它会立即退出(可以理解为它没有事情可做了)。
FOUNDATION_EXPORT NSRunLoopMode const NSDefaultRunLoopMode;
FOUNDATION_EXPORT NSRunLoopMode const NSRunLoopCommonModes; // 不是实际运行的模式,是一个标记位
UIKIT_EXTERN NSRunLoopMode const UITrackingRunLoopMode;
主线程的 RunLoop 里有两个预置的 Mode:NSDefaultRunLoopMode 和 UITrackingRunLoopMode。这两个 Mode 默认都已经添加到 commonModes 中。
NSDefaultRunLoopMode 是 App 平时所处的模式,UITrackingRunLoopMode 是 ScrollView 滑动时的模式。
当创建一个 Timer 并加到 NSDefaultRunLoopMode 后,Timer 会得到重复回调;但此时滑动一个 ScrollView,RunLoop 会以 UITrackingRunLoopMode 运行,这时 Timer 就不会被回调。
当需要 Timer 在两个 Mode 中都能得到回调,可以使用 RunLoop.current.add(timer, forMode: .common),此时这个 timer 被添加到 RunLoop 的 _commonModeItems 里,并同步给 commonModes 的所有成员:
void CFRunLoopAddTimer(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopTimerRef rlt, CFStringRef modeName) {
if (modeName == kCFRunLoopCommonModes) {
CFSetRef set = rl->_commonModes ? CFSetCreateCopy(kCFAllocatorSystemDefault, rl->_commonModes) : NULL;
CFSetAddValue(rl->_commonModeItems, rlt);
if (NULL != set) {
CFTypeRef context[2] = {rl, rlt};
/* add new item to all common-modes */
CFSetApplyFunction(set, (__CFRunLoopAddItemToCommonModes), (void *)context);
CFRelease(set);
}
}
}
static void __CFRunLoopAddItemToCommonModes(const void *value, void *ctx) {
CFStringRef modeName = (CFStringRef)value;
CFRunLoopRef rl = (CFRunLoopRef)(((CFTypeRef *)ctx)[0]);
CFTypeRef item = (CFTypeRef)(((CFTypeRef *)ctx)[1]);
if (CFGetTypeID(item) == CFRunLoopSourceGetTypeID())
{
CFRunLoopAddSource(rl, (CFRunLoopSourceRef)item, modeName);
}
else if (CFGetTypeID(item) == CFRunLoopObserverGetTypeID())
{
CFRunLoopAddObserver(rl, (CFRunLoopObserverRef)item, modeName);
}
else if (CFGetTypeID(item) == CFRunLoopTimerGetTypeID())
{
CFRunLoopAddTimer(rl, (CFRunLoopTimerRef)item, modeName);
}
}
Observer
RunLoop 可以监听的状态:
/* Run Loop Observer Activities */
typedef CF_OPTIONS(CFOptionFlags, CFRunLoopActivity) {
kCFRunLoopEntry = (1UL << 0),
kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers = (1UL << 1),
kCFRunLoopBeforeSources = (1UL << 2),
kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting = (1UL << 5),
kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting = (1UL << 6),
kCFRunLoopExit = (1UL << 7),
kCFRunLoopAllActivities = 0x0FFFFFFFU
};
源码分析
怎么找源码的调用入口呢?我们通过查看一个点击事件的调用堆栈:
找 CFRunLoopRunSpecific 函数,这个函数就相当于入口了:
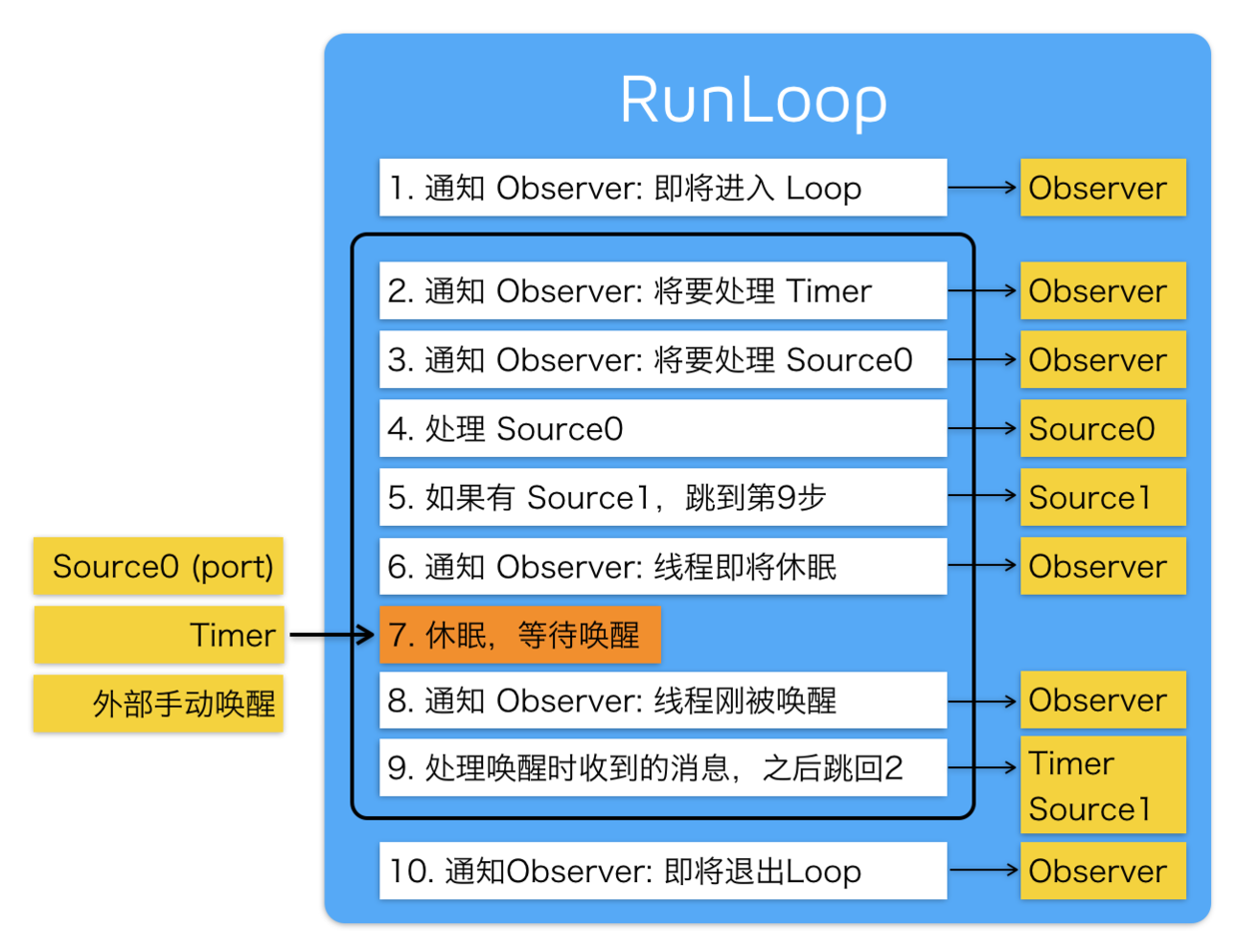
SInt32 CFRunLoopRunSpecific(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFStringRef modeName, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean returnAfterSourceHandled) {
// 外部传 modeName,指定 RunLoop 运行的模式
CFRunLoopModeRef currentMode = __CFRunLoopFindMode(rl, modeName, false);
CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode = rl->_currentMode;
rl->_currentMode = currentMode;
// 通知 Observers:进入 RunLoop
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopEntry)
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopEntry);
// 处理 RunLoop 要做的事情,返回结果
result = __CFRunLoopRun(rl, currentMode, seconds, returnAfterSourceHandled, previousMode);
// 通知 Observers:退出 RunLoop
if (currentMode->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopExit)
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, currentMode, kCFRunLoopExit);
return result;
}
static int32_t __CFRunLoopRun(CFRunLoopRef rl, CFRunLoopModeRef rlm, CFTimeInterval seconds, Boolean stopAfterHandle, CFRunLoopModeRef previousMode) {
int32_t retVal = 0;
do {
// 通知 Observers:即将处理 Timers
if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers)
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeTimers);
// 通知 Observers:即将处理 Sources
if (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeSources)
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeSources);
// 处理 Blocks,即 CFRunLoopPerformBlock(_:_:_:)
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
// 处理 Source0
Boolean sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSources0(rl, rlm, stopAfterHandle);
if (sourceHandledThisLoop) {
// 再次处理 Blocks
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
}
// 判断有无 Source1
if (MACH_PORT_NULL != dispatchPort && !didDispatchPortLastTime)
{
// 处理 Source1,即 Port 相关
if (__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(dispatchPort, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, 0, &voucherState, NULL))
{
goto handle_msg;
}
}
// 通知 Observers:即将进入休眠
if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting))
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopBeforeWaiting);
__CFRunLoopSetSleeping(rl);
do {
// 等待 Port 消息来唤醒当前线程
// RunLoop 等待在这个函数这里
__CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(waitSet, &msg, sizeof(msg_buffer), &livePort, poll ? 0 : TIMEOUT_INFINITY, &voucherState, &voucherCopy);
// 知道这里会有break跳出这个循环就可以了
} while (1);
// 通知 Observers:结束休眠
__CFRunLoopUnsetSleeping(rl);
if (!poll && (rlm->_observerMask & kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting))
__CFRunLoopDoObservers(rl, rlm, kCFRunLoopAfterWaiting);
// 路径一:结束休眠后,判断是什么原因被唤醒的,做相应的处理
handle_msg: // 路径二:前面 goto 跳过来的
if (modeQueuePort != MACH_PORT_NULL && livePort == modeQueuePort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_TIMER();
// 处理 Timers
__CFRunLoopDoTimers(rl, rlm, mach_absolute_time());
} else if (livePort == dispatchPort) {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_DISPATCH();
// 处理 GCD
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__(msg);
} else {
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP_FOR_SOURCE();
// 处理 Source1
sourceHandledThisLoop = __CFRunLoopDoSource1(rl, rlm, rls, msg, msg->msgh_size, &reply) || sourceHandledThisLoop;
}
// 处理 Blocks
__CFRunLoopDoBlocks(rl, rlm);
// 设置返回值
if (sourceHandledThisLoop && stopAfterHandle) {
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunHandledSource;
}
else if (timeout_context->termTSR < mach_absolute_time()) {
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunTimedOut;
}
else if (__CFRunLoopIsStopped(rl)) {
__CFRunLoopUnsetStopped(rl);
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
}
else if (rlm->_stopped) {
rlm->_stopped = false;
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunStopped;
}
else if (__CFRunLoopModeIsEmpty(rl, rlm, previousMode)) {
retVal = kCFRunLoopRunFinished;
}
} while (0 == retVal); // 如果结果不为0,就退出循环,返回了
return retVal;
}
流程图:
处理不同事件的函数
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_AN_OBSERVER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_TIMER_CALLBACK_FUNCTION__
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_BLOCK__
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE0_PERFORM_FUNCTION__
__CFRUNLOOP_IS_CALLING_OUT_TO_A_SOURCE1_PERFORM_FUNCTION__
GCD 的绝大多数工作是不用依赖 RunLoop 的,只有派发任务到主队列时,才会由 RunLoop 通过 __CFRUNLOOP_IS_SERVICING_THE_MAIN_DISPATCH_QUEUE__ 函数处理。
用户的触摸事件是由 Source1 捕获、再交给 Source0 处理的。Source1 可以理解为内核管理的进程间通信,Source0 可以理解为 App 管理的应用内部事件处理。
线程是如何休眠的
上面提到 RunLoop 等待在 __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort 这个函数里,找到它的实现:
static Boolean __CFRunLoopServiceMachPort(mach_port_name_t port, mach_msg_header_t **buffer, size_t buffer_size, mach_port_t *livePort, mach_msg_timeout_t timeout, voucher_mach_msg_state_t *voucherState, voucher_t *voucherCopy) {
kern_return_t ret = KERN_SUCCESS;
for (;;) {
ret = mach_msg(msg, MACH_RCV_MSG | (voucherState ? MACH_RCV_VOUCHER : 0) | MACH_RCV_LARGE | ((TIMEOUT_INFINITY != timeout) ? MACH_RCV_TIMEOUT : 0) | MACH_RCV_TRAILER_TYPE(MACH_MSG_TRAILER_FORMAT_0) | MACH_RCV_TRAILER_ELEMENTS(MACH_RCV_TRAILER_AV), 0, msg->msgh_size, port, timeout, MACH_PORT_NULL);
CFRUNLOOP_WAKEUP(ret);
if (MACH_MSG_SUCCESS == ret) {
*livePort = msg ? msg->msgh_local_port : MACH_PORT_NULL;
return true;
}
}
}
mach_msg 是一个系统调用,可以向目标端口发送 mach 消息,或者从目标端口接收 mach 消息,关于系统调用:
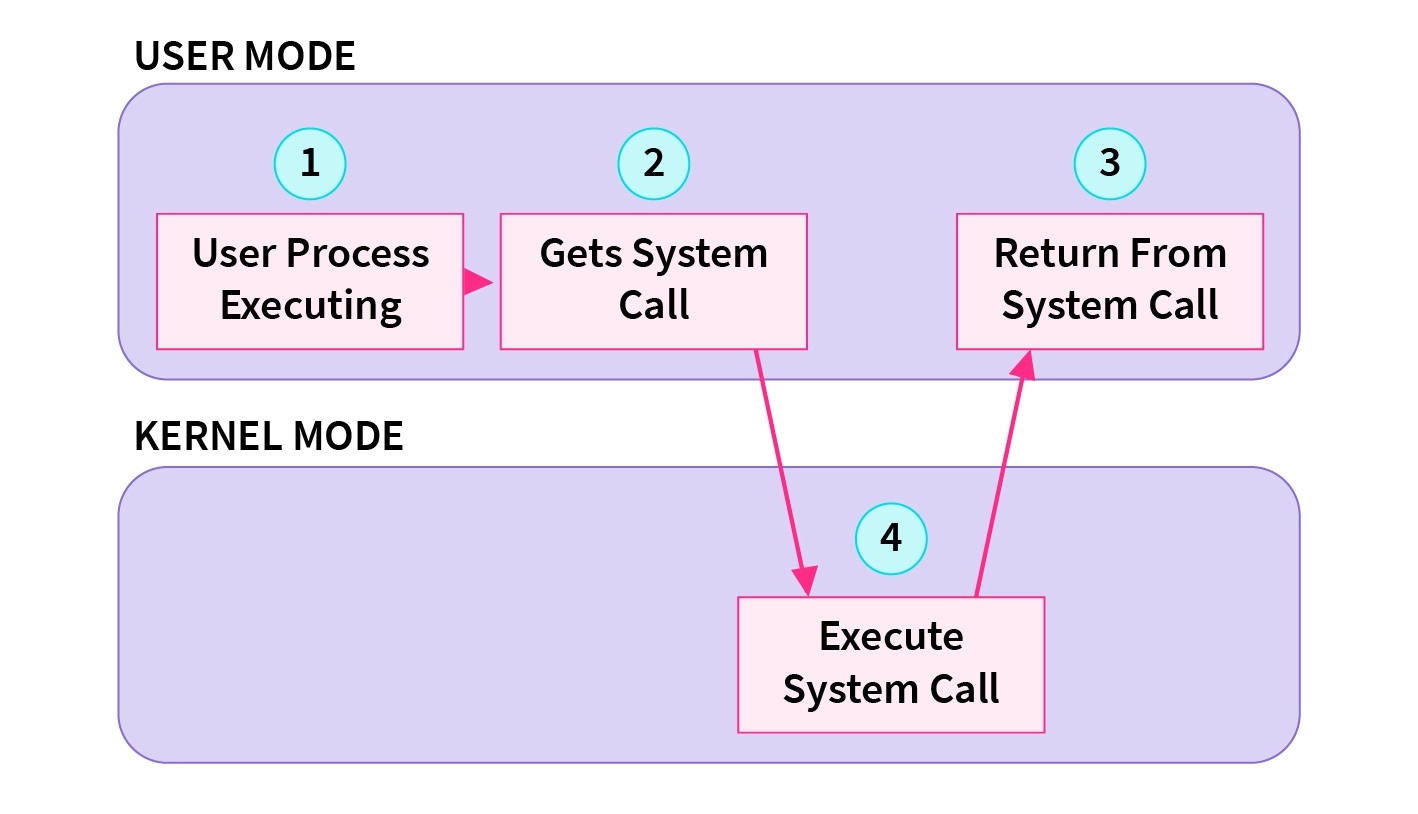
RunLoop 休眠实际上是调用操作系统的底层函�数 mach_msg,操作系统会由用户态切换到内核态,由内核将线程挂起并等待目标端口的 mach 消息。当接收到消息时,由内核唤醒线程并继续处理。
performSelector
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector;
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)object;
- (id)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(id)object1 withObject:(id)object2;
Sends a specified message to the receiver and returns the result of the message. 以上三个方法等价于直接调用。
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(nullable id)anArgument afterDelay:(NSTimeInterval)delay;
Invokes a method of the receiver on the current thread using the default (runloop) mode after a delay. 创建一个 Timer 并添加到当前线程的 RunLoop 中。所以如果当前线程没有 RunLoop,则这个方法会失效。
- (void)performSelectorOnMainThread:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(nullable id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
- (void)performSelector:(SEL)aSelector onThread:(NSThread *)thr withObject:(nullable id)arg waitUntilDone:(BOOL)wait;
- (void)performSelectorInBackground:(SEL)aSelector withObject:(nullable id)arg;
Invokes a method of the receiver on the specified thread using the default (runloop) mode. 创建一个 Timer 并加到对应线程的 Runloop 中,同样的,如果对应线程没有 RunLoop 该方法也会失效。
autoreleasepool
进入 RunLoop 时,创建一个 autoreleasepool;
RunLoop 进入休眠之前,会先释放掉 autoreleasepool,然后创建一个新的 autoreleasepool;
退出 RunLoop 时,释放掉 autoreleasepool
当一个对象调用 autorelease 方法时,会将这个对象放到栈顶的释放池自动释放池中。
iOS 5 引入 ARC 后,release、retain、retainCount、autorelease 等函数被禁止调用,编译器在合适的地方自动插入指令做了这项工作
autoreleasepool 是以 AutoreleasePoolPage 为结点的双向链表来实现的,主要通过下列三个函数完成:
- objc_autoreleasepoolPush
- objc_autoreleasepoolPop
- objc_autorelease
for (int i = 0; i < 10e5; i++) {
NSString *filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"10-14-Day-6k" ofType:@"jpg"];
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
NSLog(@"%@", image);
}
以上代码会 OOM:
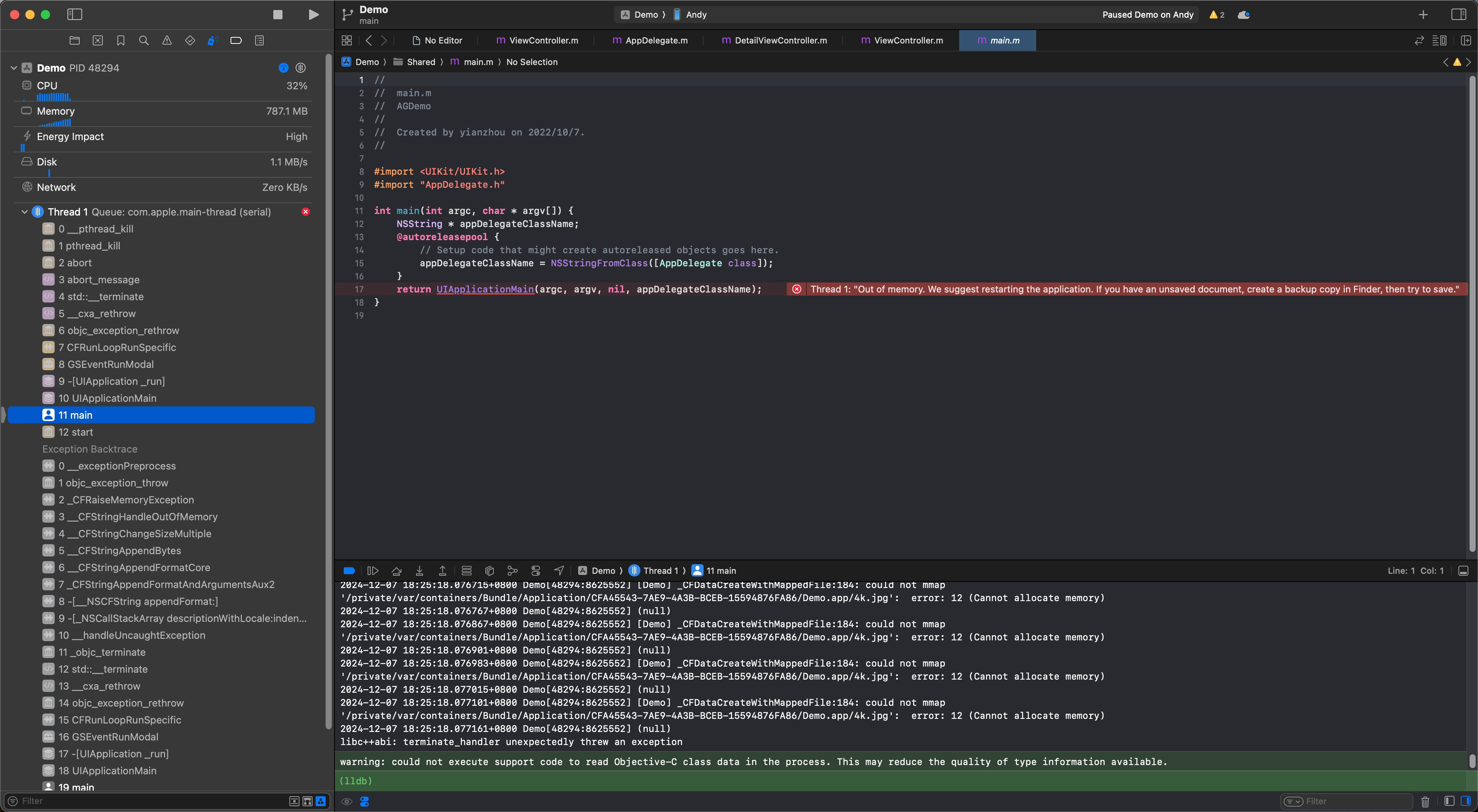
// 降低内存峰�值
for (int i = 0; i < 10e5; i++) {
@autoreleasepool {
NSString *filePath = [[NSBundle mainBundle] pathForResource:@"10-14-Day-6k" ofType:@"jpg"];
UIImage *image = [[UIImage alloc] initWithContentsOfFile:filePath];
NSLog(@"%@", image);
}
}
以上代码内存非常平稳:
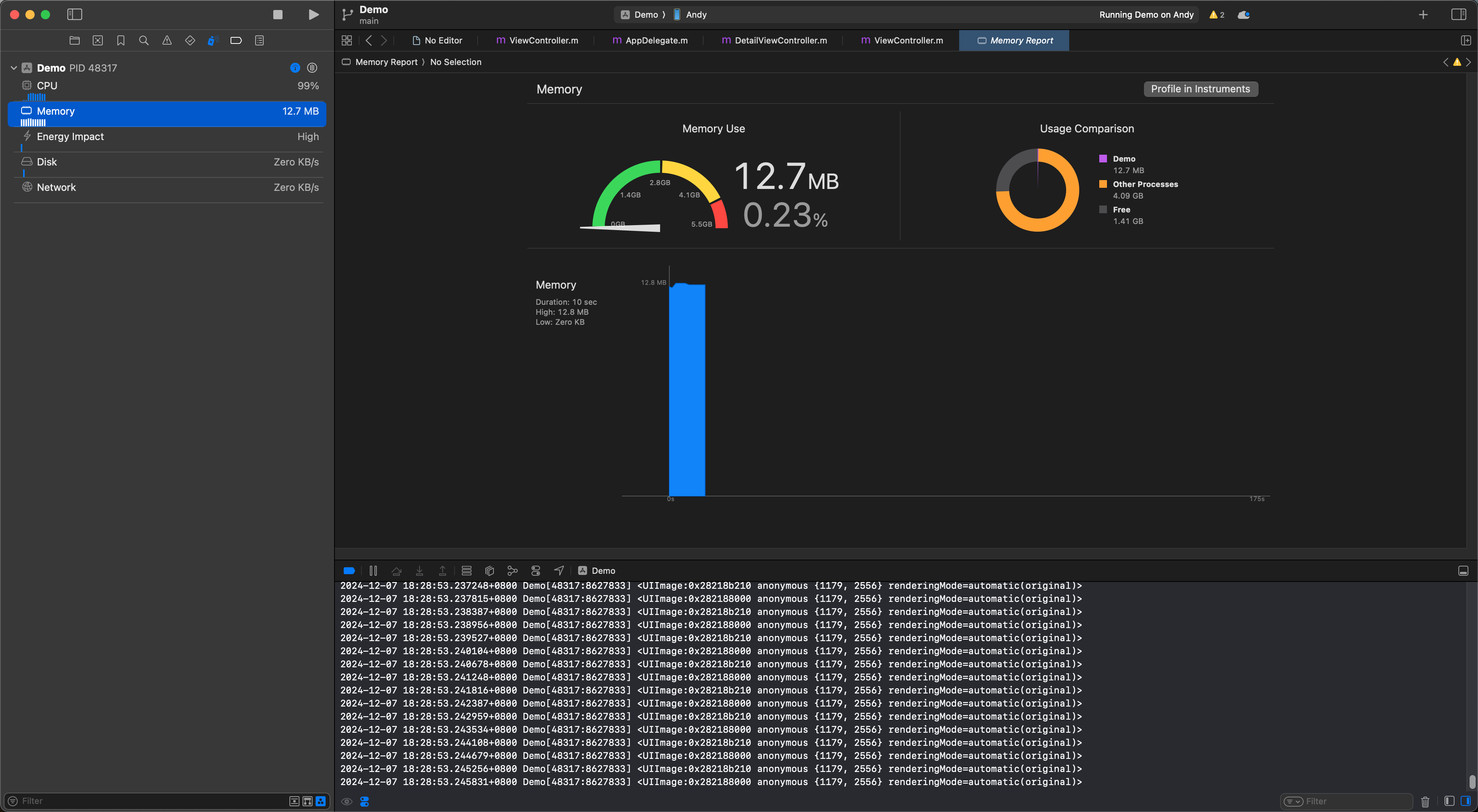
所以,autorelease 在 ARC 不能用;@autoreleasepool看情况用;那么__autoreleasing什么时候用呢?
构造一个很大的链表,在 head 释放时,它的属性 next 会先释放,如此递归下去会造成 Stack Overflow 引发 EXC_BAD_ACCESS:
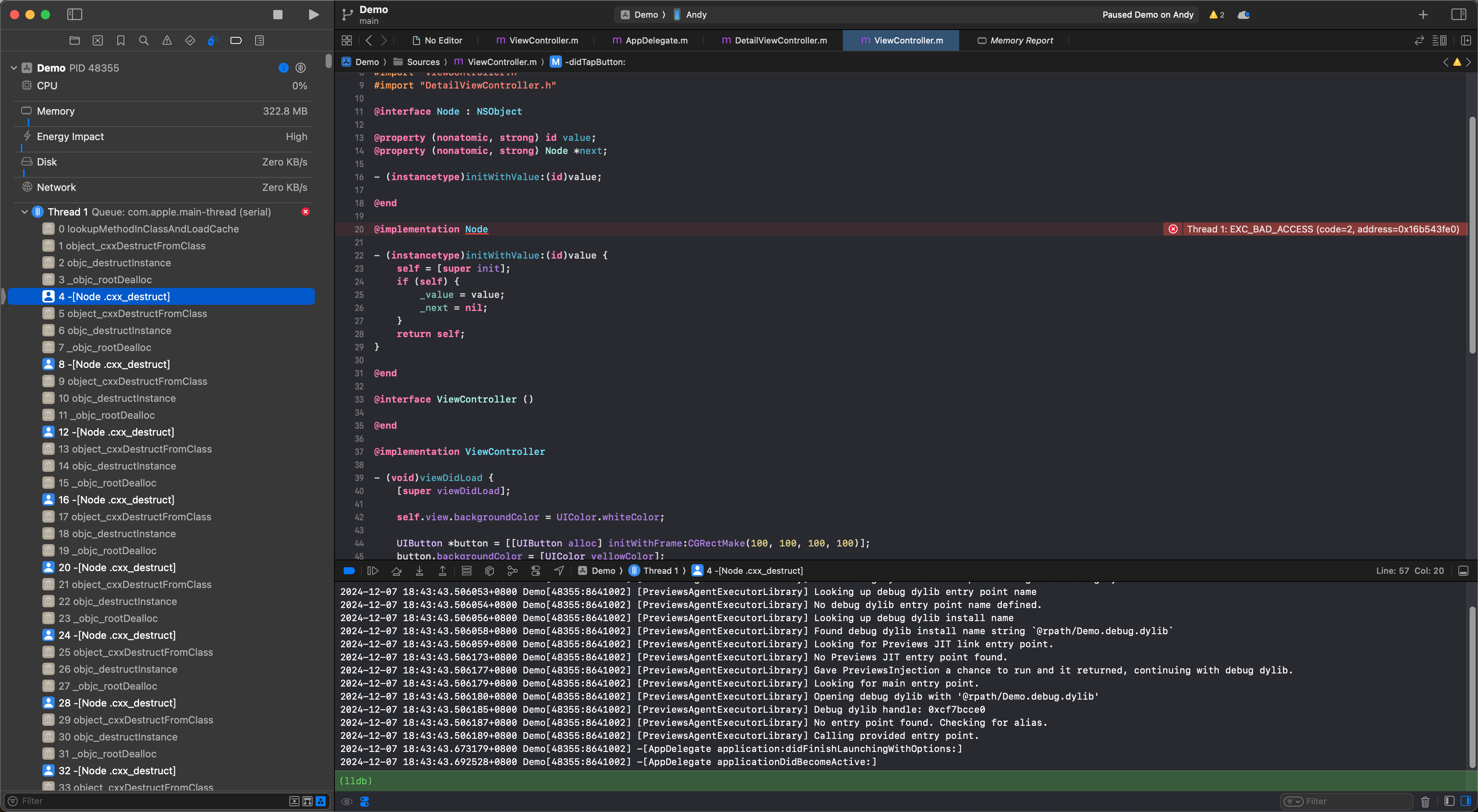
解决方法是使用__autoreleasing将next的释放交给 autoreleasepool 管理: