Dart Concurrency
异步
Asynchronous programming: futures, async, await | Dart
Dart supports concurrent programming with async-await, isolates, and classes such as Future and Stream.
A promise to eventually provide an int value is typed as Future<int>. A promise to provide a series of int values has the type Stream<int>.
The synchronous File method readAsStringSync() reads a file synchronously, blocking until the file is either fully read or an error occurs.
The asynchronous equivalent, readAsString(), immediately returns an object of type Future<String>. At some point in the future, the Future<String> completes with either a string value or an error.
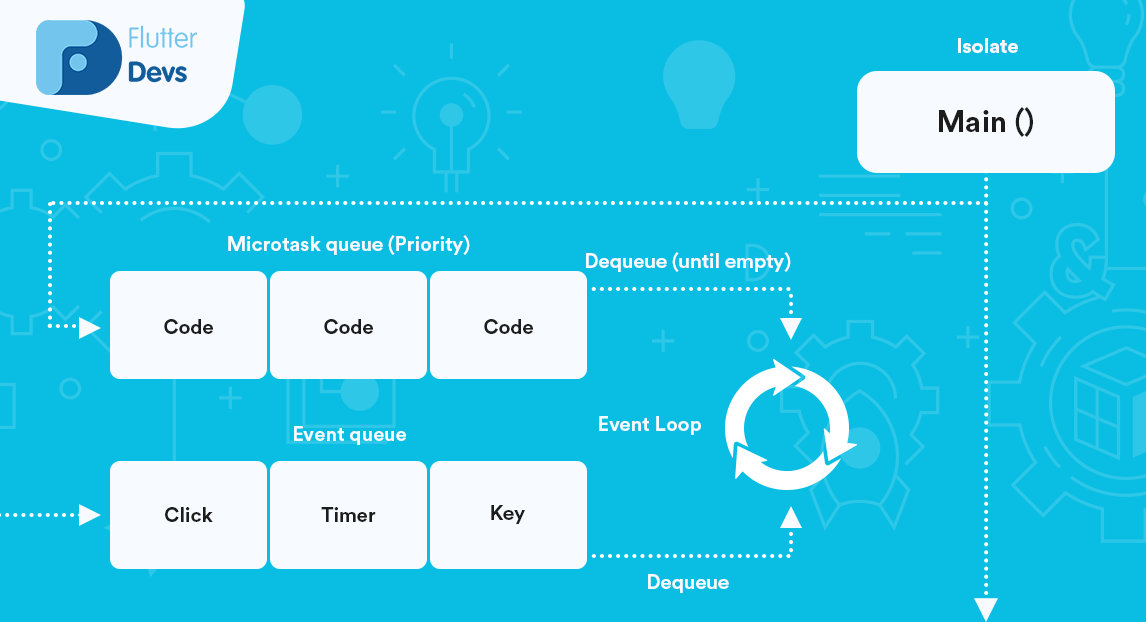
JavaScript 只有一个线程;Dart 里面,每个线程都被封装在一个 Isolate 里面。
Future 就相当于 JavaScript 里面的 Promise。
Dart asynchronous programming: Isolates and event loops | by Kathy Walrath | Dart | Medium
Event Loop 可以防止主线程被阻塞,保持主线程的响应。Future 调用会把闭包放进 Event Queue 里面;Dart 还保留了更优先的 Microtask Queue,一般不要使用。
由于 Dart 的单线程模型,如果你真的有很大的计算量要运行,就算你派发到 Event Queue 里面,最终还是要占用主线程来计算,可能导致阻塞,此时你就需要创建 Isolate,用多线程来解决问题。
示例
import 'dart:async';
void main() {
print("main 1");
// 这些会被放到 eventQueue
Future(() => print("event 1"));
Future.delayed(Duration.zero, () => print("event 2"));
Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1), () => print("event 3"));
// then是在future完成时立刻执行,不会再添加microtask
Future.delayed(const Duration(seconds: 1)).then((value) {
scheduleMicrotask(() => print("then microtask"));
print("then 1");
}).then((value) => print("then 2"));
print("main 2");
// 这些会被放到 microtaskQueue
scheduleMicrotask(() => print("microtask 1"));
Future.microtask(() => print("microtask 2"));
Future.value(1).then((value) => print("microtask 3")); // 已经完成的future使用then,会被添加到microtask
print("main 3");
// 这些会立即执行
Future.sync(() => print("sync 1"));
Future.value(getName());
print("main 4");
}
String getName() {
print("sync 2");
return "mikko";
}
The async and await keywords provide a declarative way to define asynchronous functions and use their results.
import 'dart:async';
void main() {
future1();
future2();
}
void future1() {
// future 有三种�状态:未完成、已完成、出错
getOne()
.then((value) {
print(value);
return ++value;
})
.then((value) => print(value))
.catchError((err) => print(err))
.whenComplete(() => print("complete"));
}
Future<int> getOne() {
// throw Exception("error");
return Future.value(1);
// return Future.error(Exception("error"));
}
void future2() async {
try {
int number = await getTwo();
print(number);
print(++number);
} catch (err) {
print(err);
}
}
Future<int> getTwo() async {
throw Exception("error");
return 2;
}